Pain
Conventional Medical Treatments for a Traumatic Brain Injury

What is a traumatic brain injury?
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a type of brain damage that occurs as a result of an injury to the head. This type of injury may be non-penetrative, such as a blow to the head, or penetrative, such as a gunshot wound. The severity of a TBI depends on various factors, and the lasting effects can range from a few days to permanent brain damage or, in severe cases, death. A concussion is the most common type of traumatic brain injury.
Severity classifications of a traumatic brain injury
The effect that a traumatic brain injury has on brain function is typically classified as mild, moderate or severe. The severity of the injury determines which type of treatment is appropriate.
Immediate treatments
Any TBI, regardless of the severity level, requires prompt medical attention. This involves maintaining blood supply, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, while preventing further injuries to the head and neck. TBI medical treatments may include medications, surgery, and rehabilitation therapies.
Medications
Certain medications may be prescribed in an effort to minimize secondary damage to the brain immediately following the injury. These medications may include the following:
- Anti-seizure drugs
A moderate or severe TBI increases the risk of having a seizure the first week following the incident. Anti-seizure medications may be prescribed to avoid further brain damage that could result if a seizure occurs. The use of anti-seizure drugs may be utilized longer if a seizure does transpire. - Coma-inducing medicine
A TBI may increase pressure in the brain, leaving blood vessels unable to supply the brain cells with adequate levels of oxygen. A comatose brain requires less oxygen to function; therefore, a coma may be induced until the body is stable. - Diuretics
Diuretics reduce the amount of fluid in the body’s tissues and increase urine output. This medication can be given through an IV in order to help reduce the pressure inside the brain. - Triptans
Medications called triptans might be prescribed for post-traumatic headaches or migraines. They work by calming pain nerves that are overactive.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery is needed to properly treat a TBI. Surgical procedures may include the following:
- Skull fracture repair
Surgery may be necessary to repair severe fractures in the skull. This is especially true if pieces of the skull are lodged in the brain. - Opening a window in the skull
If a TBI causes increased pressure in the skull, surgery may be needed that creates a window in the skill. This drains cerebrospinal fluid that has accumulated and allows more space for swollen tissues. - Hematoma (blood clot) removal
Blood clots can place pressure on the brain, which can damage the brain tissue. Surgery to remove blood clots can minimize this damage. - Bleeding in the brain
A TBI can result in brain bleeding. If this is the case, surgery might be necessary to stop the bleeding.
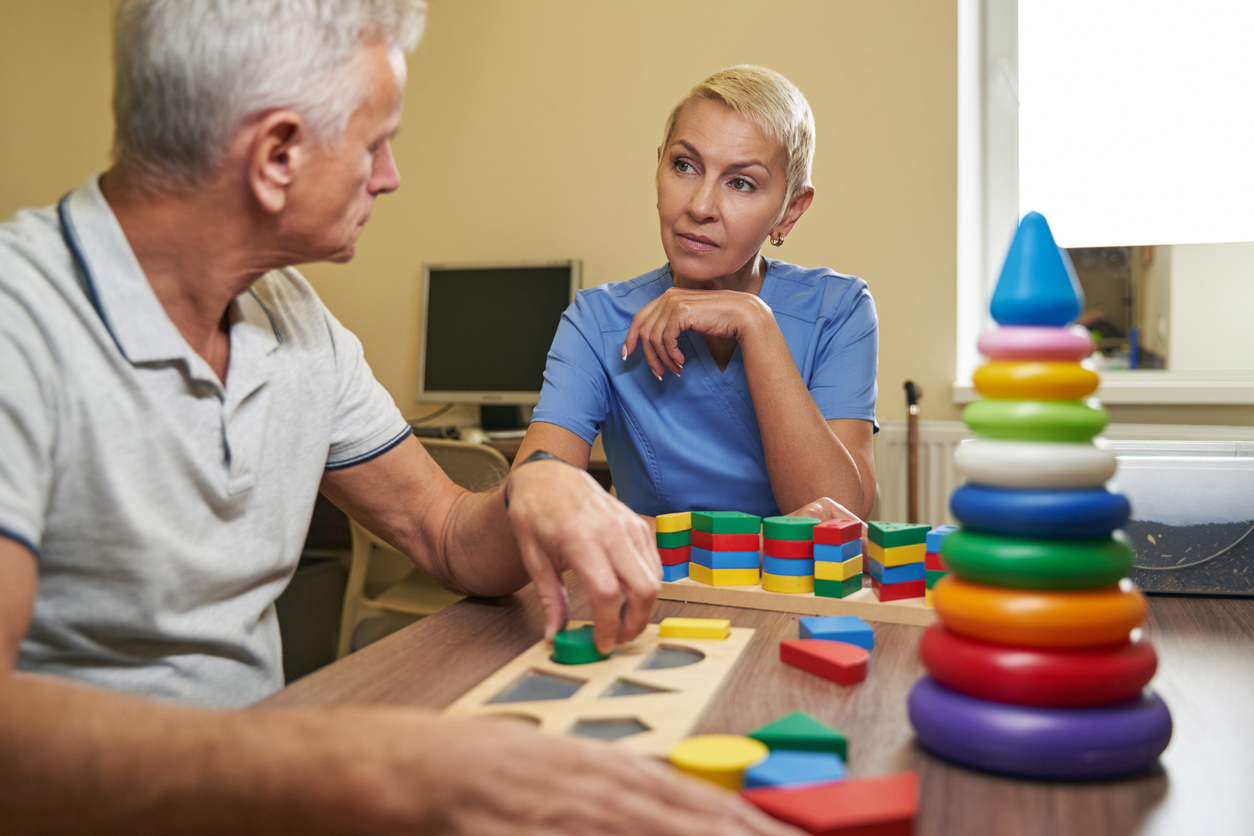
Rehabilitation
For those who have had moderate to severe TBI, rehabilitation therapy is often necessary for recovery. The goal of this treatment is to regain basic skills that may be lost as a result of a TBI, such as walking, talking, bathing, returning to work, and other tasks. Rehabilitation frequently begins in the hospital and then continues either through outpatient services, an inpatient rehabilitation unit, or a residential treatment facility. Types of rehabilitation therapy may include the following:
- Speech therapy
Speech therapy can help with the formation of words, speech and communication. It could include the use of assistive devices, such as augmentative and alternative communication (AAC). Treatment for difficulty swallowing may also be completed. - Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy helps with learning how to perform daily tasks, such as cooking, cleaning, bathing, and getting dressed. This can include the use of different assistive devices, such as tools to pull buttons through buttonholes or a device to assist putting on socks. - Physical therapy
The main goals of physical therapy (PT) are to provide pain management, improve mobility, maximize functionality, implement injury recovery, and prevent future damage. In addition, a physical therapist may also help an individual acquire and learn to properly use assistive devices, such as wheelchairs, artificial limbs, canes, walkers, etc. - Psychological therapy
A TBI can often cause chemical imbalances in the brain. This may result in behavioral and emotional changes. Psychological therapy can help improve coping skills, wellbeing, and relationships with others. - Vocational counseling
This type of program is intended to help with returning to work following a TBI. A vocational counselor can assist in finding work opportunities and accommodations that may be needed. - Cognitive therapy
A TBI can cause the loss of certain cognitive functions. Cognitive therapy is intended to help with regaining skills with memory, learning, judgment, attention and perception.