Treatments
Training and Accreditation Requirements for Physical Therapists in Canada and the United States

What is a physical therapist?
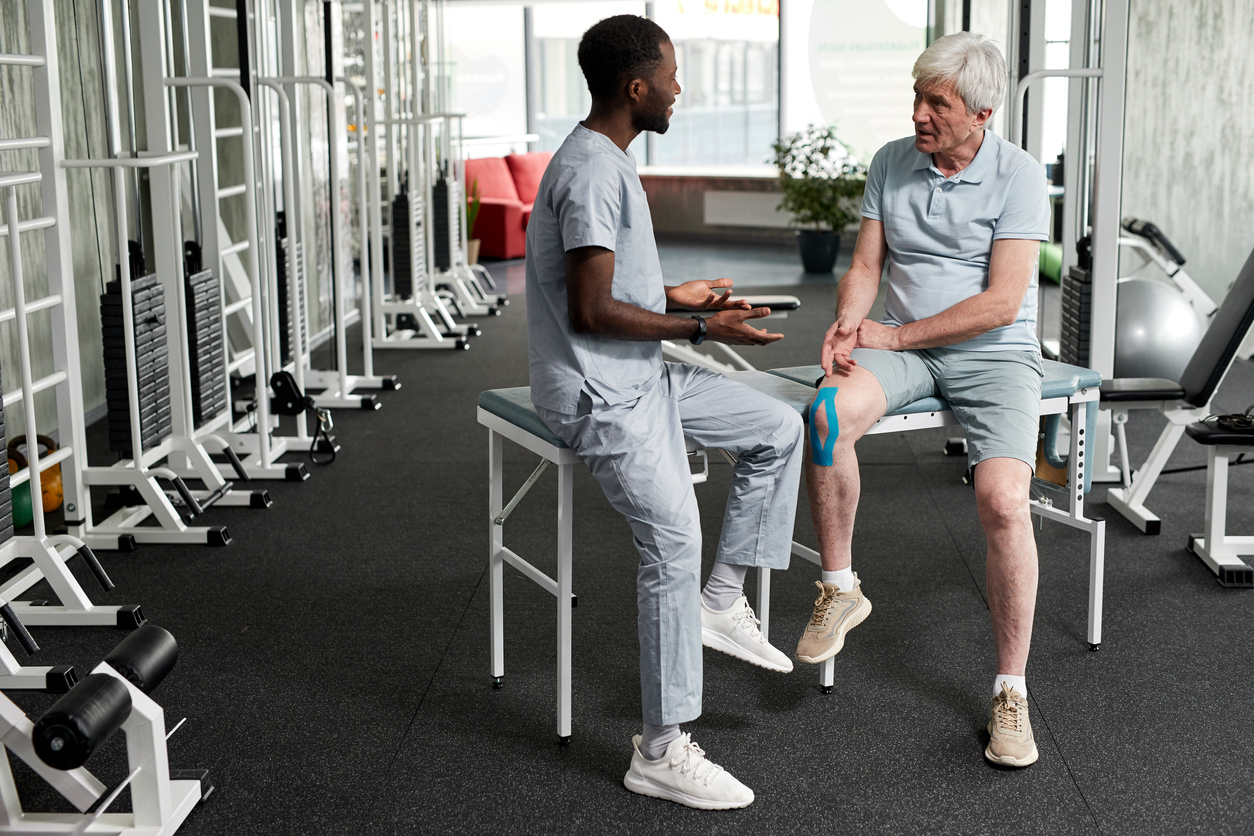
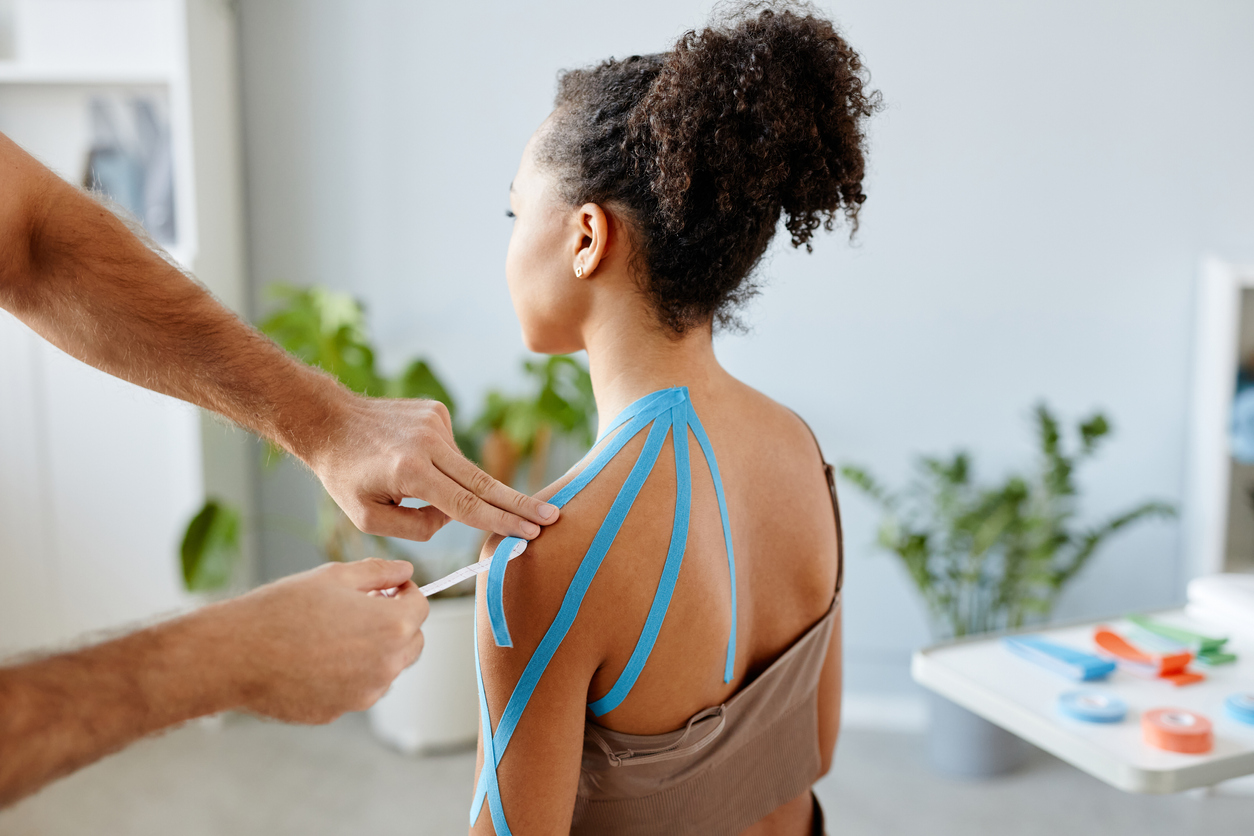
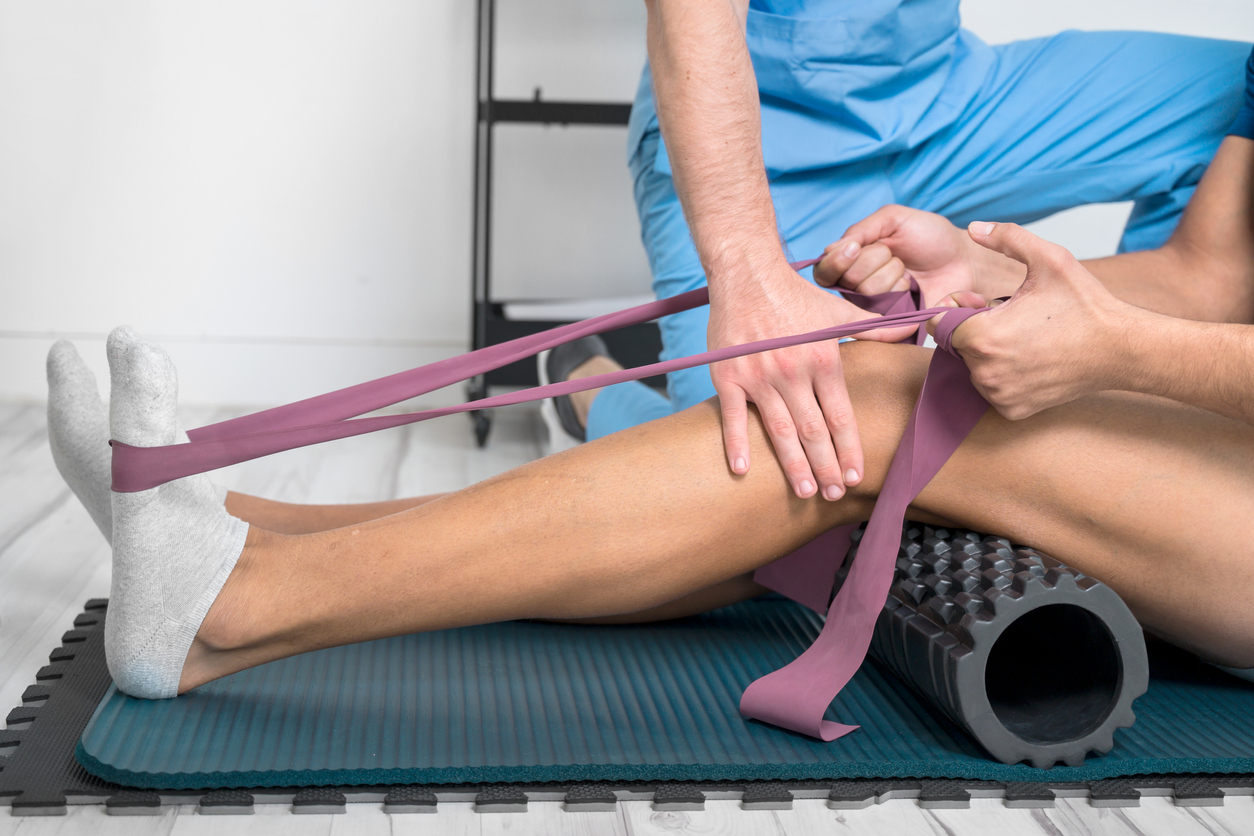
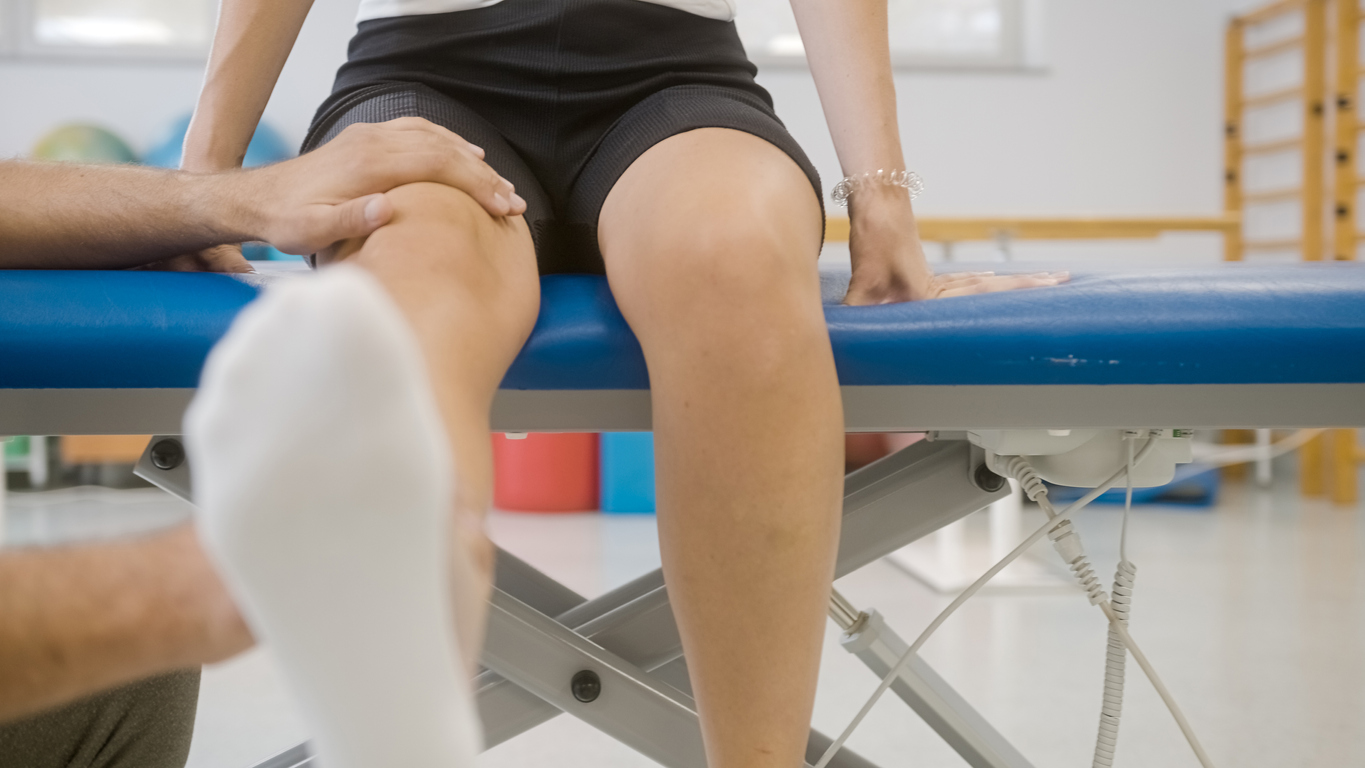
The goal of physical therapy is to improve movement and range of motion. A physical therapist is a type of health care professional trained to help individuals maximize their mobility and functionality. The clients they treat may be recovering from an injury or illness, or have specific conditions (chronic and acute). A physical therapist evaluates the person and condition in order to treat illnesses and injuries related to the musculoskeletal (bones and muscles), neurological (brain), cardiopulmonary (heart and lungs) and integumentary (skin) systems.
What does a physical therapist do?
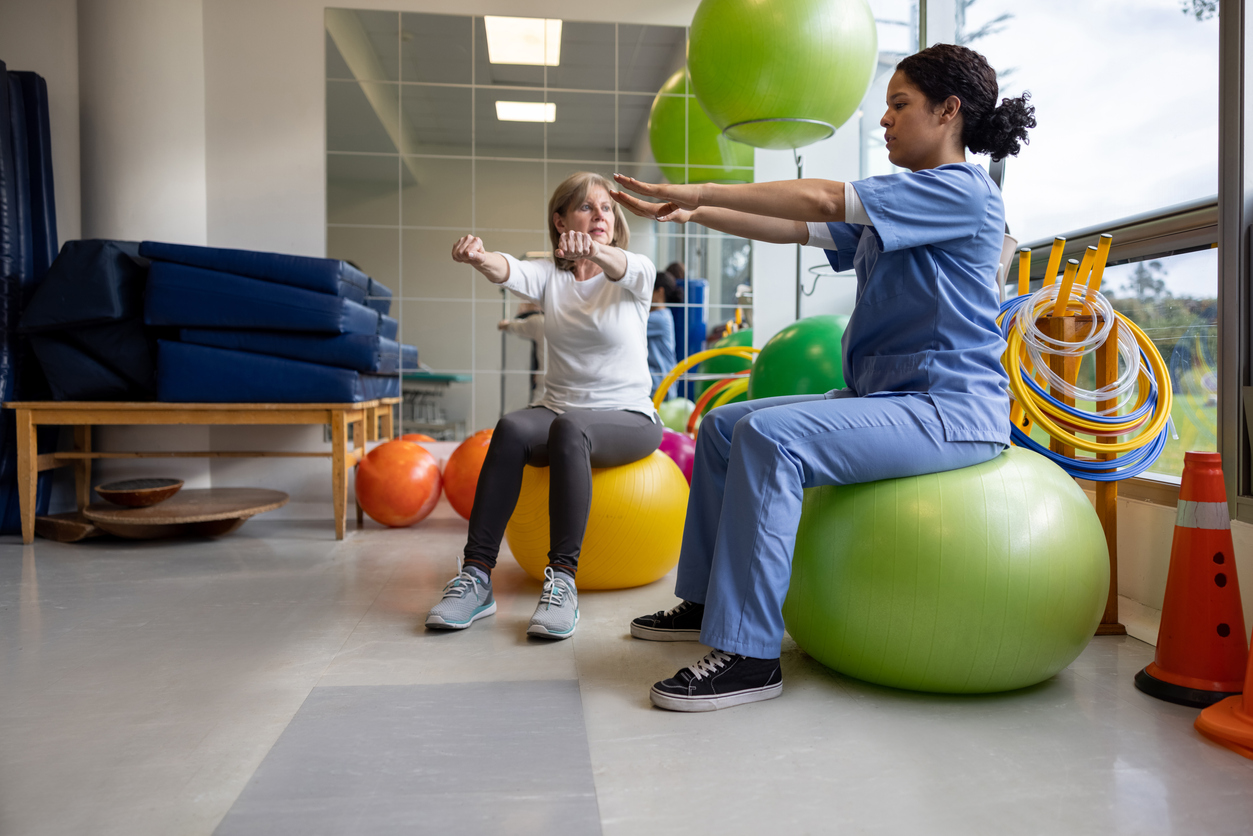
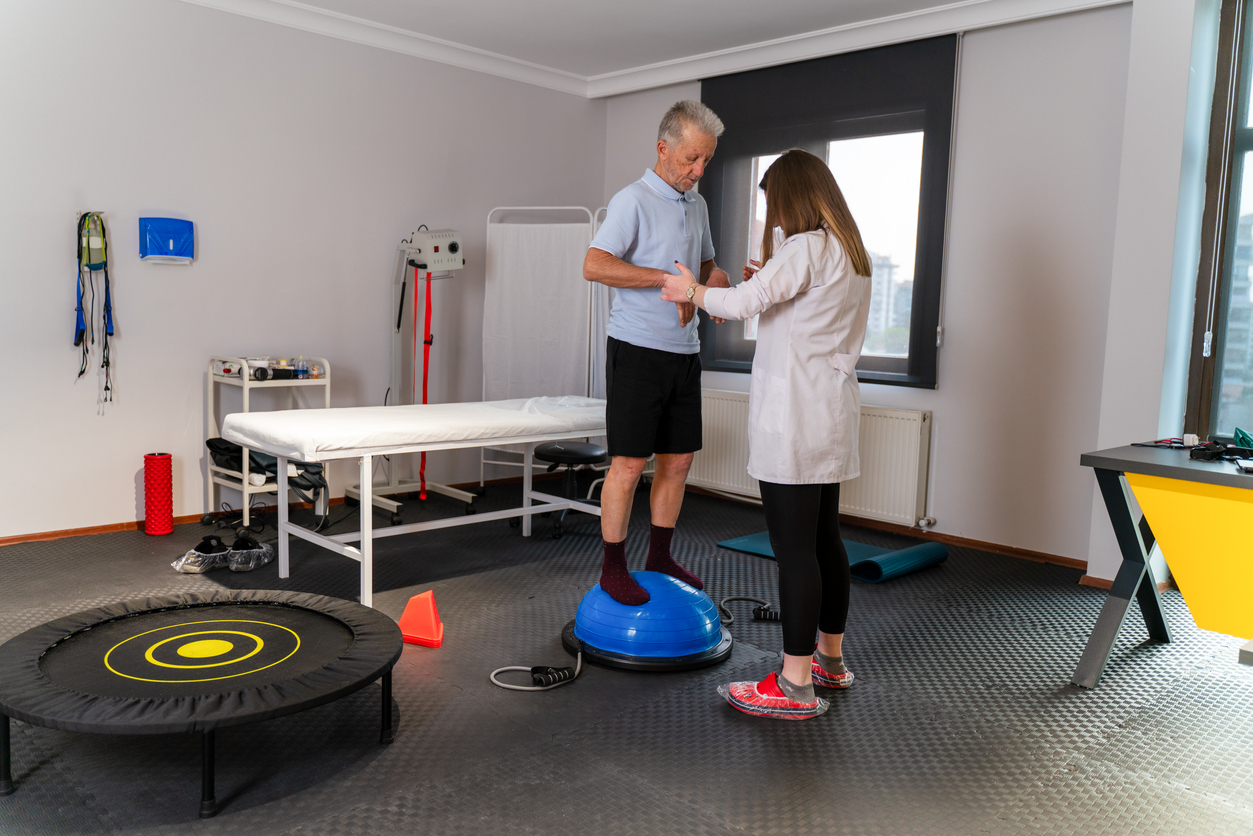
After assessing the individual’s physical ability and health condition, a physical therapist then develops an individual plan that adopts techniques to provide pain management, improve mobility, implement injury recovery, and prevent future damage. They may utilize equipment, or incorporate exercise, stretching, and other hands-on techniques, to treat the condition.
United States requirements for a physical therapist
To become a physical therapist in the United States, a doctor of physical therapy (DPT) degree must be obtained from the Commission on Accreditation in Physical Therapy Education (CAPTE), which is an accredited physical therapist education program recognized by the US Department of Education. Although they are not medical doctors, they also must have a bachelor’s degree. Additionally, they must pass a state licensure exam for the state in which they wish to practice physical therapy.
DPT programs typically take three years to complete. Program content may include the following:
- Anatomy
- Behavioral sciences
- Biomechanics
- Cardiovascular and pulmonary
- Clinical reasoning
- Communication
- Endocrine and metabolic
- Ethics and values
- Evidence-based practice
- Exercise physiology
- Kinesiology
- Management science
- Musculoskeletal systems
- Neuroscience
- Pathology
- Physiology
- Sociology
The DPT curriculum normally consists of 80% class and lab study and 20% clinical education. An estimated 27.5 weeks include final clinical experience.
After earning a DPT degree, an individual may opt to participate in a residency or fellowship program, although this is not required. They can also become a board-certified specialist in a specific area through the American Board of Physical Therapy Specialties.
Canada requirements for a physical therapist
In Canada, a College of Physiotherapist exists in each province or territory that manages physiotherapists and physiotherapy assistants. They are also in charge of licensing and discipline.
In order to become a physiotherapist, a master’s degree in one out of 15 accredited programs across Canada is required. Typically, these programs last two years. The actual degree title varies according to the University. For example, Master’s of Physical Therapy or Master’s of Science in Physical Therapy. To apply for the program, individuals must have first completed a bachelor’s degree and various prerequisite courses as part of that degree.
Following the master’s program, individuals must take the Physiotherapy Competency Exam (PCE). The PCE has both written and clinical portions. After successfully passing this exam, they apply to the College of Physiotherapy where they live for an “Independent Practice Certificate of Registration.”
Individuals who received training outside of Canada can become physiotherapists. The first step is to contact the Canadian Alliance of Physiotherapy Regulators (CAPR). CAPR will review education details in relation to Canada’s current education requirements for physical therapy.
Additional sources: Medical News Today, American Physical Therapy Association, Canadian Alliance of Physiotherapy Regulators (CAPR), College of Physiotherapists of Ontario, and Canadian Council of Physiotherapy University Programs