Pain
Types of Eczema
1 person found this helpful
Print
Share
Save
What is eczema?
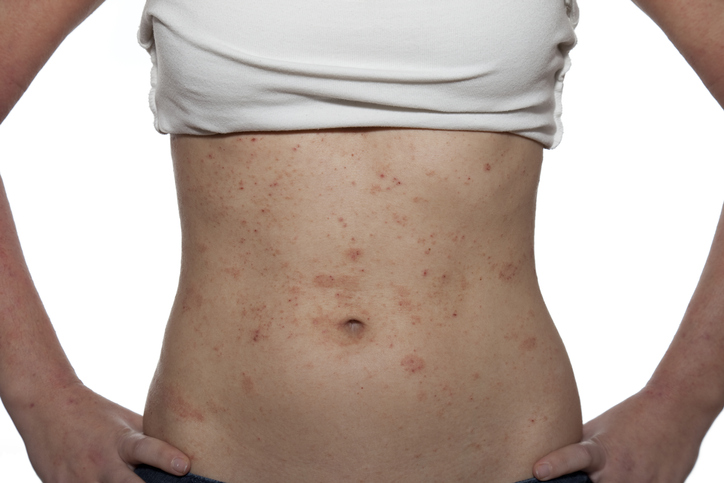
Eczema is the medical term used for a group of health conditions characterized by inflamed, irritated, itchy patches of skin. It can develop at any age, and approximately one in 10 people will develop some type of eczema in their lifetime. It is generally a chronic (long-term) condition that involves periodic flare-ups; however, it can also be acute (short-term).
What are the types of eczema?
There are several types of eczema that affect the skin. Types of eczema include the following:
- Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema; actually, the two terms are often used interchangeably. Symptoms typically develop during childhood and improve during adulthood; however, it can develop at any age. Atopic dermatitis frequently occurs in individuals who also have allergies, hay fever, or asthma. It most commonly affects the skin on the face, hands, feet, the inside bends of the elbows, or behind the knees.
- Dyshidrotic eczema involves the formation of small blisters on the hands and feet. The blisters may be itchy and painful and eventually develop into scaly patches.
- Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to contact with a chemical or other substance. The skin reaction is typically red and very itchy. There are two types of contact dermatitis: irritant contact eczema and allergic contact eczema. Irritant contact eczema can develop from frequent hand-washing or contact with chemicals. Allergic contact eczema develops when the skin reacts to an allergy-triggering substance, such as poison ivy, nickel, certain cosmetics, or other substances.
- Hand eczema affects only the hands. It most commonly occurs in individuals who work in professions that require the repetitive use of chemicals that irritate the skin on the hands (e.g., cleaning, hairdressing, healthcare, etc.). The skin on the hands becomes dry, red, and itchy, and cracks or blisters may develop.
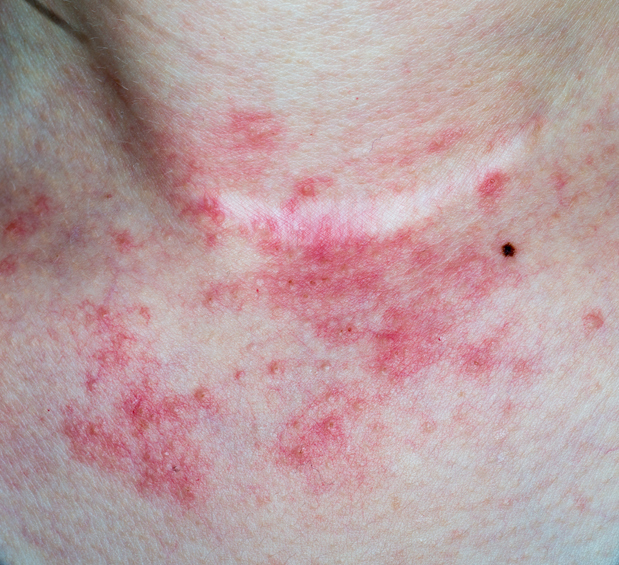
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic form of eczema that affects the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, and behind the ears. It can also appear on or around folds of the body, such as the navel, groin, armpits or breasts. Symptoms include white or yellow scaly, flaky patches of skin.
- Nummular eczema involves the formation of round, coin-shaped spots on the skin. The spots appear red and can be itchy or scaly. The spots commonly occur on the legs, backs of the hands, forearms, lower back, or hips. Nummular eczema can be triggered by various things, such as an insect bite; exposure to cold, dry air; and exposure to chemicals (e.g., formaldehyde) or metals (e.g., nickel).
- Stasis dermatitis, also known as venous eczema or gravitational dermatitis, occurs when fluid leaks from weakened veins into the skin. This causes redness, swelling and itching. Stasis dermatitis develops due to poor circulation in the lower legs.
- Neurodermatitis, also known as lichen simplex chronicus, presents with a patch of itchy skin that becomes even itchier after scratching. This itch-scratch cycle can cause the skin to become thick and leathery. Neurodermatitis is typically a life-long condition; treatment aims to stop the urge to scratch (which often becomes a habit or occurs unconsciously).