Pain
Alternative and Complementary Treatment Options for Eczema

What is eczema?
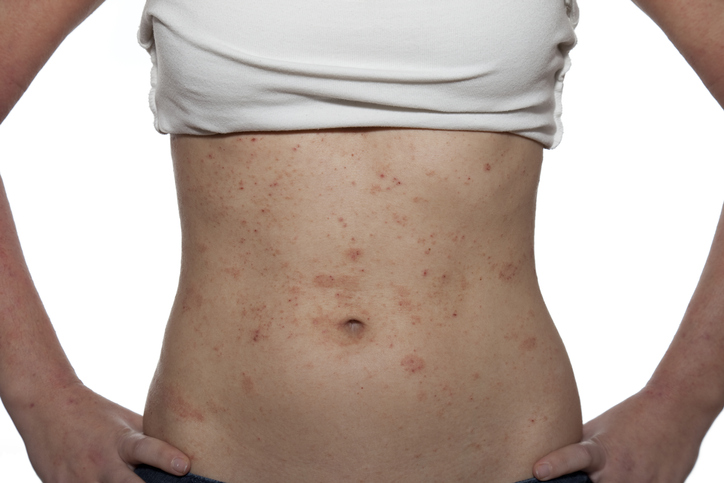
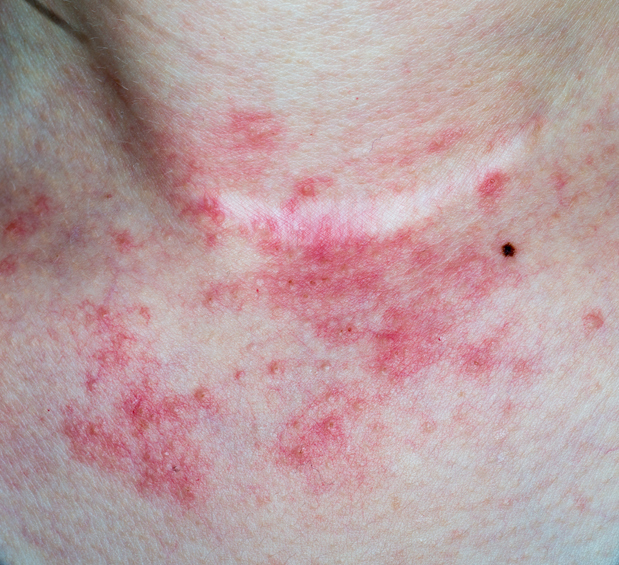
Eczema is the medical term used for a group of health conditions characterized by inflamed, irritated, itchy patches of skin. It can develop at any age, and approximately one in 10 people will develop some type of eczema in their lifetime. It is generally a chronic (long-term) condition that involves periodic flare-ups; however, it can also be acute (short-term).
There are various types of eczema. However, atopic dermatitis is the most common form, and the two terms are often used interchangeably.
Alternative and complementary treatments
In addition to conventional medical treatments for eczema, several alternative and complementary treatments are also available. These treatments include oils, supplements, acupressure or acupuncture, and relaxation techniques.
- Natural oils such as sunflower seed oil and virgin coconut oil can be applied to the skin to help reduce eczema symptoms. Sunflower seed oil has anti-inflammatory properties and can improve skin hydration. Virgin coconut oil has anti-inflammatory and antibiotic properties.
- Witch hazel has been used for centuries as a topical treatment to calm inflamed skin and reduce itching. It is an astringent that comes from the witch hazel shrub.
- Calendula cream is an herbal remedy that helps hydrate the skin and is thought to improve blood flow to areas of inflammation. It may also help fight infection.
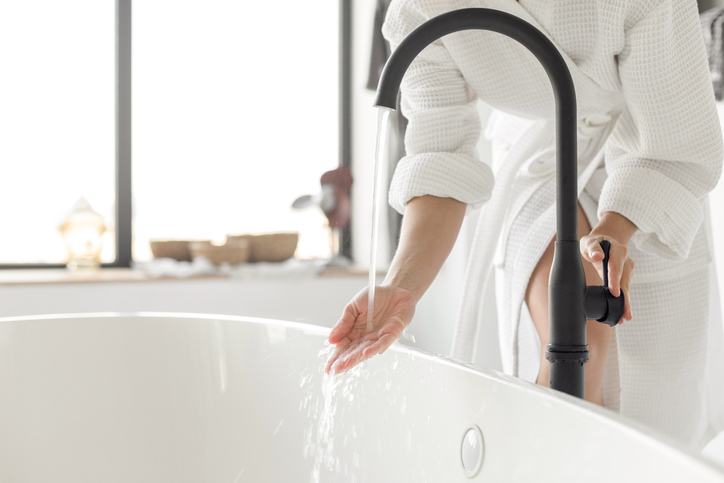
- Colloidal oatmeal is a powder made from finely ground oats. When added to a lukewarm bath, colloidal oatmeal can soften the skin and reduce itching.
- Evening primrose oil is derived from the evening primrose plant. It can be applied topically to soothe the skin or taken internally to reduce inflammation. The oil contains omega-6 fatty acids and gamma-linoleic acid, both of which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Topical vitamin B12 has proven to be an effective treatment for symptoms of eczema in both adults and children. A commercial version of topical vitamin B12 is not available, so it must be made at a compounding pharmacy. More information can be found on the National Eczema Association’s website at www.nationaleczema.org.
- Vitamin D supplements may help reduce symptoms of eczema.
- Probiotics may be beneficial for many inflammatory conditions, including eczema. Probiotics may reduce inflammation and itching. Probiotic supplements that contain Lactobacillus plantarum bacteria improve skin barrier function and skin hydration.
- Acupuncture or acupressure may help relieve the itching associated with eczema. The acupoint that is most commonly stimulated during treatment for eczema is the Quchi point, located near the crease of the elbow. Acupuncture may also balance levels of histamine, which can trigger symptoms of eczema.
- Stress management techniques techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, massage, hypnosis, and deep breathing, may be helpful for individuals with eczema, as stress can worsen eczema symptoms. These relaxation techniques can improve sleep, reduce itching, and improve overall quality of life.
Since some supplements and treatments have side effects or may interfere with certain medications, a medical professional should always be consulted before beginning any alternative or complementary treatments for eczema.