Pain
At-Home Treatments for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome

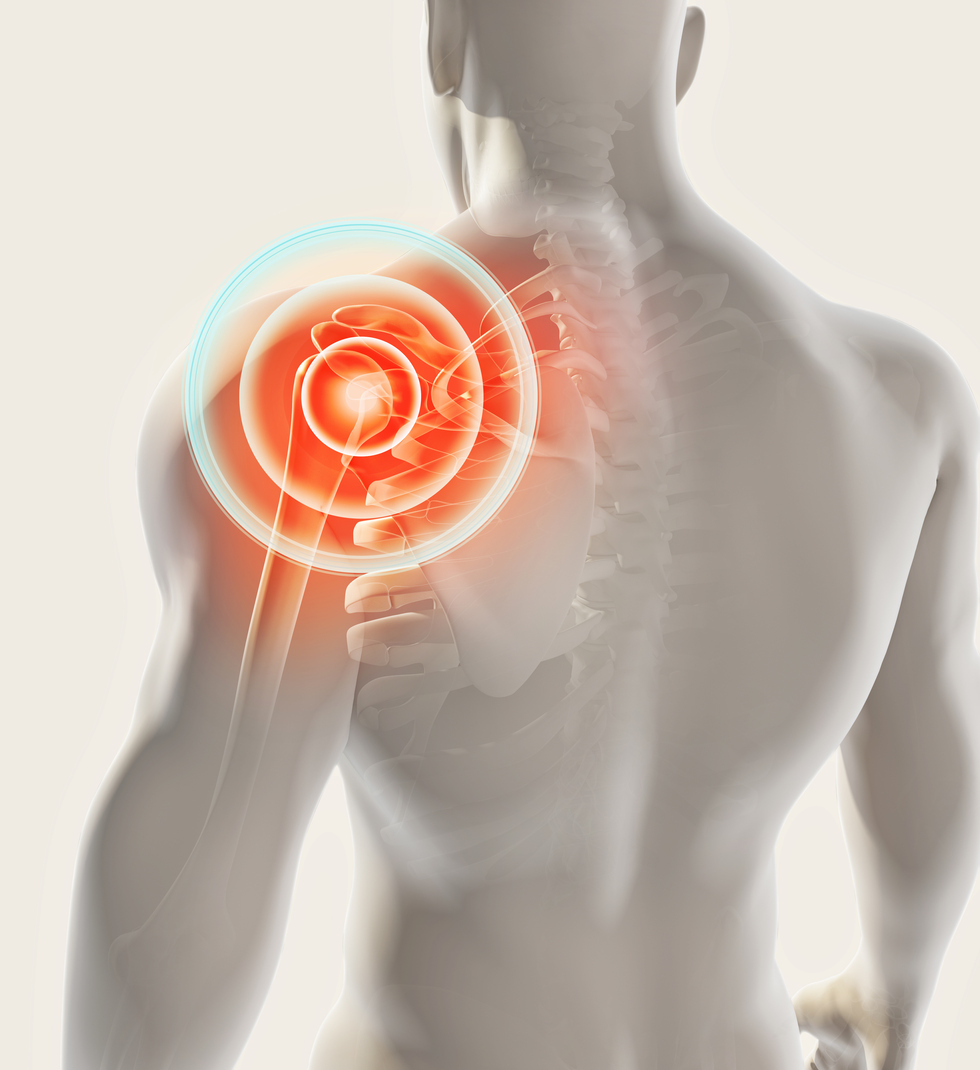
What is thoracic outlet system (TOS)?
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition in which the nerves and/or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet become compressed, irritated or injured. The thoracic outlet is a narrow space located between the collarbone and the first rib. The nerves and blood vessels that move down the arm, and the muscles from the neck to the shoulder, run through the thoracic outlet.
At-home treatments for thoracic outlet syndrome
In addition to conventional treatment plans, at-home-treatment may also minimize the symptoms of TOS. This includes over-the-counter medication, stretching, massages, temperature therapy, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle adjustments.
Medications
Over-the-counter NSAIDs, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as naproxen or ibuprofen, can relieve pain and inflammation caused by TOS. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as acetaminophen, can reduce pain.
Stretching
Moving and stretching is helpful, especially when engaging in activities that limit movement, such as office work or video games. Stretching can reduce the risk of developing TOS or ease its symptoms. Specific stretches to reduce symptoms, improve posture, and return to normal functionality can be found at the University Health Network.
Massage
A massage helps relieve muscle tension in the affected area and reduces nerve pressure that is causing pain. Massage therapy should focus on the shoulder and thoracic outlet area. Massages promote blood flow and reduce inflammation at the site impacted by TOS.
Temperature therapy
Heat therapy relaxes the stiff joints and muscles that are associated with TOS. Heat increases the temperature of the targeted area, improving circulation and blood flow. This can soothe pain in stiff joints and increase muscle flexibility. Heat therapy may involve dry heat, such as a heating pad, or moist heat, such as steamed towels.
Relaxation techniques
Relaxation techniques allow the muscles to relax, which can reduce pain resulting from TOS. Examples include meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and deep breathing.
Lifestyle adjustments
Several lifestyle changes can relieve symptoms of TOS. These include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Posture and ergonomics
Poor posture can result in TOS if the collarbones shifts and places pressure on nearby nerves. Proper posture can reduce pain associated with TOS. Ensure working areas, such as desks, have ergonomic adjustments to support proper posture. - Activities to avoid
Weight and pressure on the shoulders, such as from a heavy bag, can worsen TOS. Avoid carrying and lifting heavy objects and repetitive movements that place stress on the thoracic area. Avoid positions that involve having the arms held out or over the head for extended periods. - Sleeping positions
Sleep in a position that will not add pressure on the thoracic outlet. Avoid sleeping with the arms extended behind the head. Avoid sleeping on the stomach with the arms over the head. - Weight loss
Individuals who are overweight or obese should consider losing weight. Weight loss can relieve stress on joints and reduce symptoms associated with TOS.