Treatments
Benefits of Bee Pollen
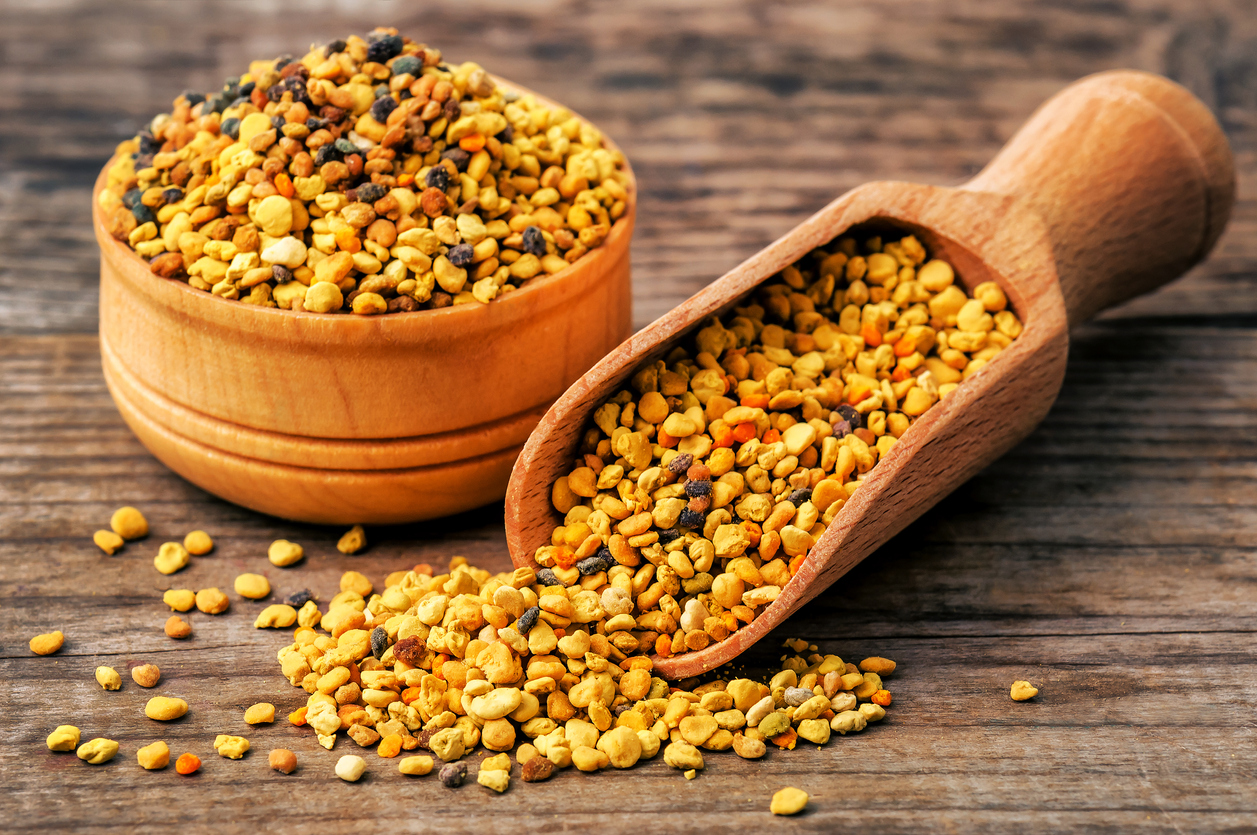

What is bee pollen?
Pollen collects on the bodies of bees when they land on flowers. Bee pollen is a mixture of bee saliva, nectar, honey and pollen. As the bees fly from one flower to another, they collect pollen balls in the sacks on their legs. They then take it back to the hive and store it in a honeycomb. The pollen ferments and feeds the bee colony.
How is bee pollen collected?
Beekeepers keep a thick comb at the entrance of the hive in order to collect the bee pollen. As the bees pass through the comb, pollen from the legs are knocked off into a bin to be collected. Bee pollen is not to be confused with natural honey, honeycomb, or bee venom.
Health benefits of bee pollen
Bee pollen contains vitamins, nutrients, minerals, protein, amino acids, lipids, antibiotics, antioxidants, and various other active substances. However, it may not be safe for individuals that are allergic to bees or wasps. The benefits of bee pollen include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Nutritional value. Bee pollen is a source of vitamins, minerals, proteins and carbohydrates. It has over 250 types of nutrients. It can be added to yogurt, smoothies, etc. Some studies have shown that bee pollen can help reduce obesity by speeding up metabolism.
- Reduced inflammation. Bee pollen has shown to help decrease inflammation and swelling by working similarly to anti-inflammatory medications. It has several compounds, such as quercetin, that reduces the production of omega-6 fatty acids, which increase inflammation.
- Increased antioxidants. Research has shown that bee pollen has high antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are natural chemicals in certain plant-based and fermented foods that protect the body from free radicals. Free radicals can cause cell damage that leads to various chronic diseases.
- Improved liver health. The liver filters and removes toxins from the blood. Bee pollen can increase liver function by boosting the liver’s antioxidant defenses. Additionally, it can also protect the liver from toxic substances and increase the healing process following liver damage.
- Lower heart disease risk factors. The risk of developing a heart disease is increased by high cholesterol and high blood lipids. Studies have shown that bee pollen can reduce cholesterol levels. Oxidized lipids lump together and restrict blood vessels. The antioxidants in bee pollen protect the lipids from oxidation.
- Boosted immune system. Bee pollen can boost the immune system by killing potentially harmful bacteria with its antimicrobial, antifungal and antiviral properties. The severity and onset of allergies is also reduced by bee pollen. Mast cells grow in the skin, airway, gastrointestinal tract, and bone marrow. They are blood cells that play a part in the immune system, and are also involved in allergic reactions. Bee pollen may reduce the activation of these mast cells.
- Eased menopause symptoms. Menopause normally results in various symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, insomnia, and irritability. Bee pollen may reduce menopausal symptoms. It may also be safer than antihormonal medications.
- Faster healing. The antimicrobial properties of bee pollen can prevent infection, which drastically slows the healing time for burns, cuts and scrapes. It boosts blood circulation to promote healing. Bee pollen also moistens the skin.
- Treating or preventing cancer. Bee pollen may be beneficial in the prevention of certain cancers, such as leukemia, prostate or colon. It may inhibit tumor growth and stimulate the death of cells.
- Diminished stress. Stress negatively impacts the nervous system. Bee pollen can encourage blood flow to the nervous system, which can reduce stress and strengthen the nervous system.
Dosage
Bee pollen is an unproven treatment; therefore, no standard dosage exists. A health care professional should be consulted for advice on how much to take.
Side effects
Bee pollen appears to be safe, except for those who are allergic to bees or wasps. Potential side effects include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Itching
- Shortness of breath
- Hives
- Swelling
- Allergic reaction
- Redness
- Anaphylaxis
- Bleeding, especially if taken with certain blood thinners
- Increased heart rate
- Lightheadedness
- Death, although rare
Where to get bee pollen
Bee pollen supplements can be found at many health food stores. Several large retail stores also sell bee pollen. It may be an ingredient in dietary supplements or products used for eczema or diaper rash.
Warnings
Bee pollen should not be used by those with pollen or bee or wasp sting allergies. Avoid bee pollen if taking blood thinners. In addition, children, pregnant women, or women who are breastfeeding should not take bee pollen.
Takeaway
Additional research is needed to prove the benefits of bee pollen. Most studies have been performed on animals and cells. Bee pollen should always be purchased from a trusted source. A health care professional should be consulted prior to taking bee pollen.