Living with Chronic Pain
Diagnosing Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome

What is delayed sleep phase syndrome?
When the sleep-wake cycle is disrupted to the point that everyday activities are affected, it is considered a circadian rhythm disorder. One such disorder is delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS). This condition is characterized by at least a two-hour delay (going to sleep at a later time and waking at a later time) in comparison to a standard sleep-wake cycle. Symptoms include, but are not limited to, insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty waking in the morning, irritability, decreased alertness, and difficulty with concentration. DSPS is most common in teenagers and young adults.
It is important to note that individuals with delayed sleep phase syndrome do not choose to stay up late; their circadian rhythm, or internal clock, is delayed by two hours or more. Research suggests that genetics plays a role in the development of DSPS.
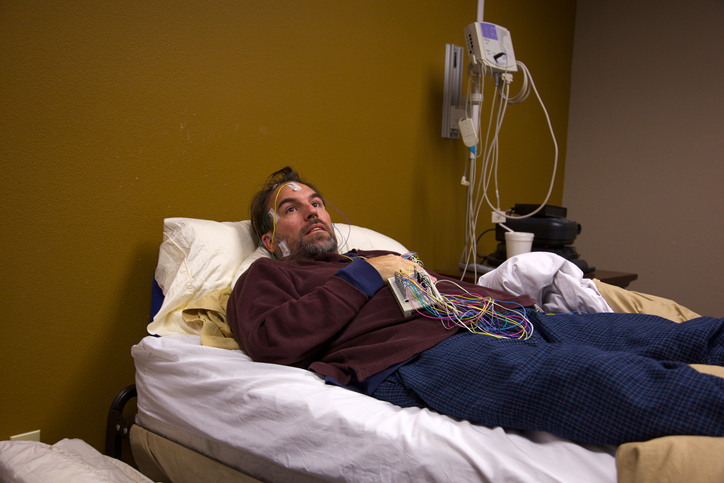
Diagnostic process
The first step in the diagnostic process is obtaining a family and medical history. A physical exam typically follows. If delayed sleep phase syndrome is suspected, one or more of the following may be recommended.
- Sleep diary
A health care provider may suggest keeping a sleep diary for a week or more to better understand personal sleep patterns. This involves logging daily sleep and wake times. - Actigraphy
An actigraphy involves wearing a small device on the wrist for several days to track sleep and wake times. The device detects motion and light exposure. - Polysomnography
Also known as a sleep study, a polysomnography may be recommended if other sleep disorders are suspected. A sleep study is typically performed overnight in a sleep center. It measures heart rate, breathing function, oxygen levels, brain activity, and eye movements during sleep. - Dim light melatonin test (DLMO)
A dim light melatonin test is a non-invasive test that assesses disturbances in circadian rhythms, such as a phase delays or advanced rhythms. Testing typically takes place between 8 p.m. and 3 a.m. in a dim environment. During this time, saliva samples are collected to measure melatonin levels. - Multiple sleep latency test (MSLT)
A multiple sleep latency test is used to identify excessive daytime sleepiness. The test involves measuring if and how fast sleep occurs when provided the opportunity to nap (every two hours) during normal wake hours. An MSLT also measures how quickly REM sleep occurs. It can help determine if another hypersomnia condition, such as narcolepsy, is responsible for symptoms.
Additional source: Ontario Sleep Clinics