Treatments
What Is Cupping?

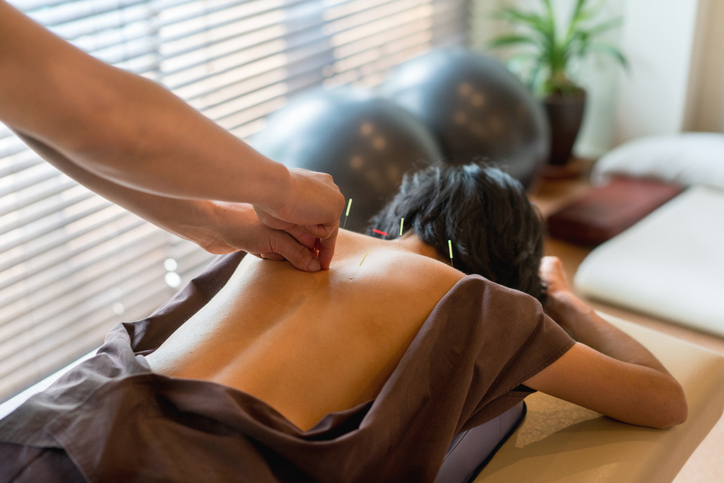
Cupping is a type of traditional Chinese medicine that has been used for thousands of years. It involves placing special cups on the skin to create suction, which increases blood flow. The goal is to reduce inflammation and promote healing. It is also thought to promote the flow of Qi (life energy) in the body and balance positive and negative qualities known as yin and yang.
What does cupping involve?
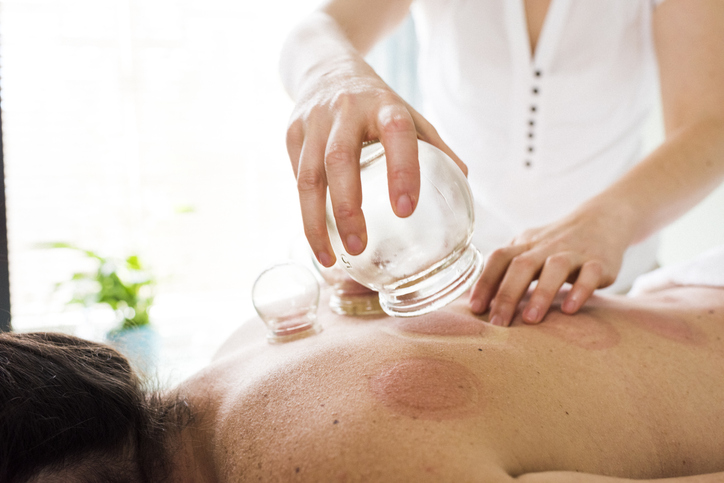
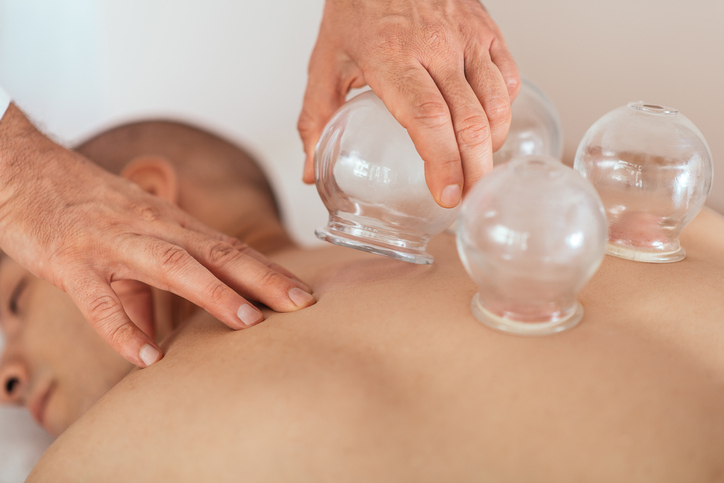
The cups used today are typically made of glass, but they can also be made of silicone, bamboo, plastic, ceramic or metal. The inside of the cup is heated and placed on the skin. As the cup cools, the skin is drawn inside the cup. The blood vessels expand, and the skin reddens. The cup is typically left in place for about five minutes.
What is the difference between wet cupping and dry cupping?
During wet cupping, the practitioner uses a scalpel to create tiny cuts in the skin after the cup is removed. A second cup is then applied to draw out a small amount of blood. Cupping without these cuts is known as dry cupping.
What are the benefits of cupping?
Cupping increases blood flow in the areas being treated. It can relieve muscle tension and is thought to reduce pain and inflammation. It may be used as an alternative treatment for back or neck pain, migraines, osteoarthritis, asthma, high blood pressure, and various other health conditions.
What are the risks of cupping?
Cupping is generally considered a safe treatment. It may leave round bruise-like marks that disappear within two weeks. Cupping should be avoided by individuals taking blood-thinning medications or anyone who has a sunburn, a skin ulcer, or any other type of skin wound.