Pain
What Is Scoliosis?
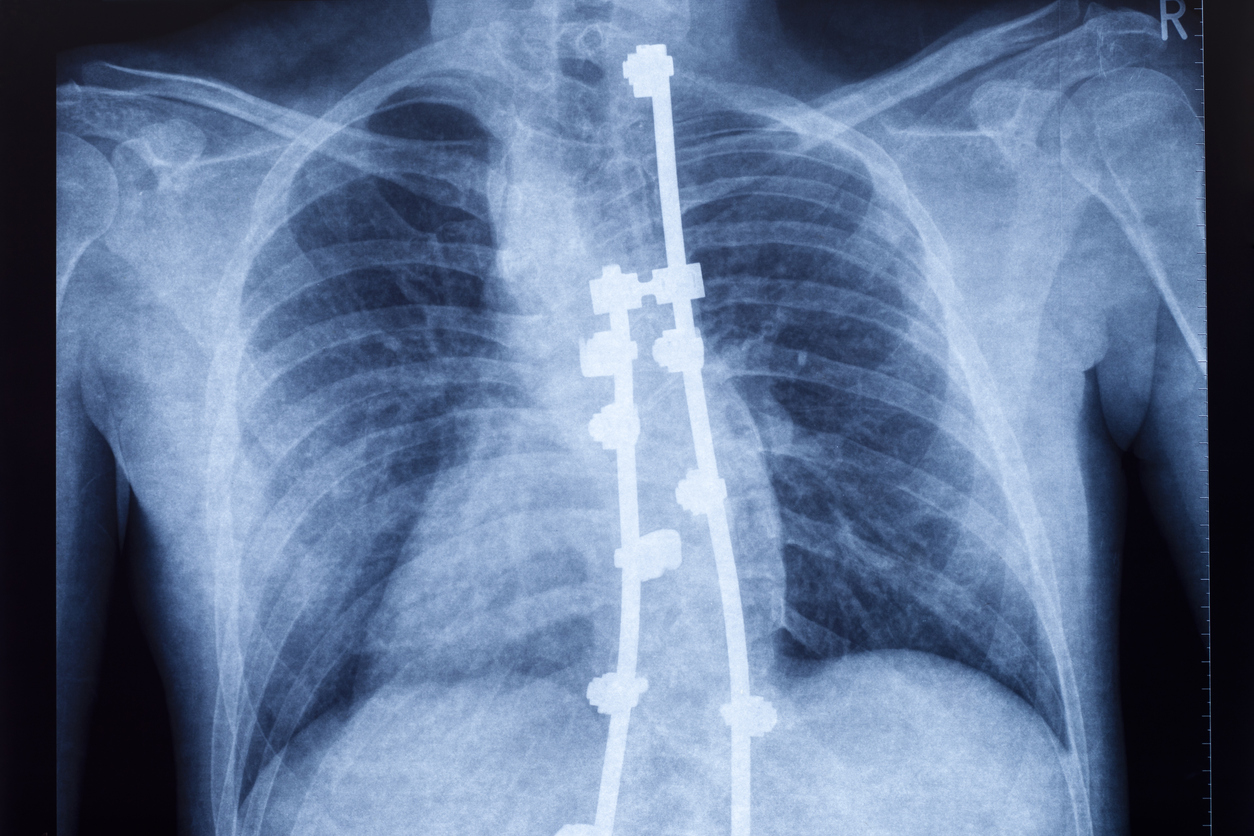
Scoliosis is defined as a sideways curvature of the spine. It is usually diagnosed in adolescents. Scoliosis is considered as a curve of at least 10 degrees to the side on an X-ray. Severe scoliosis can cause lung difficulty due to reduced space in the chest area.
Types of scoliosis
There are many types of scoliosis. The types of structural scoliosis include idiopathic, degenerative, neuromuscular and congenital.
- Idiopathic scoliosis has no known cause. This type accounts for up to 80 percent of cases.
- Degenerative scoliosis is the result of wear and tear during the aging process. It typically develops in the lower back.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis is the result of other disorders that cause damage to the muscles that support the spine. They may include cerebral palsy, a spinal cord injury, or spina bifida.
- Congenital scoliosis is rare and occurs prior to birth. The vertebrae may fail to divide or not develop completely.
Symptoms
A common symptom of scoliosis is a slight lean when standing. Other signs and symptoms include the following:
- Uneven waist
- One hip higher than the other
- Uneven shoulders
- One shoulder blade appears more prominent
- Prominence on one side of the back when bent over
- One side of rib cage juts forward
- Spine that rotates or twists
Causes
The cause of scoliosis depends upon the type. Unknown factors cause idiopathic scoliosis; however, some research shows that genetic factors may be involved in this variation. Degenerative scoliosis (also referred to as “adult scoliosis”) is caused by the degeneration of the joints in the spine that accompany the process of aging. Certain neuromuscular conditions, such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, etc., may prevent a person from walking. This can lead to neuromuscular scoliosis, which is sometimes called “myopathic scoliosis”. Scoliosis that develops prior to birth is referred to as congenital scoliosis.
Structural scoliosis can be caused by tumors, infections, or genetic conditions, including Marfan syndrome or Down syndrome. Scoliosis may also be the result of a nonstructural issue. Nonstructural scoliosis is less common, but may be caused by factors such as the following:
- Inflammation
- Muscle spasms
- Difference in leg heights
Risk factors
Genetics and family history are risk factors for idiopathic scoliosis. Minor idiopathic scoliosis is equally present in males and females; however, it is more likely to progress in females.