Pain
GABAergic Transplant as an Emerging Treatment for Neuropathic Pain

What is GABA?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It works to block chemical messages and decrease stimulation of nerve cells in the brain. Its calming effect helps to control stress, anxiety and fear. GABA also helps slow or stop certain pain signals.
How it works
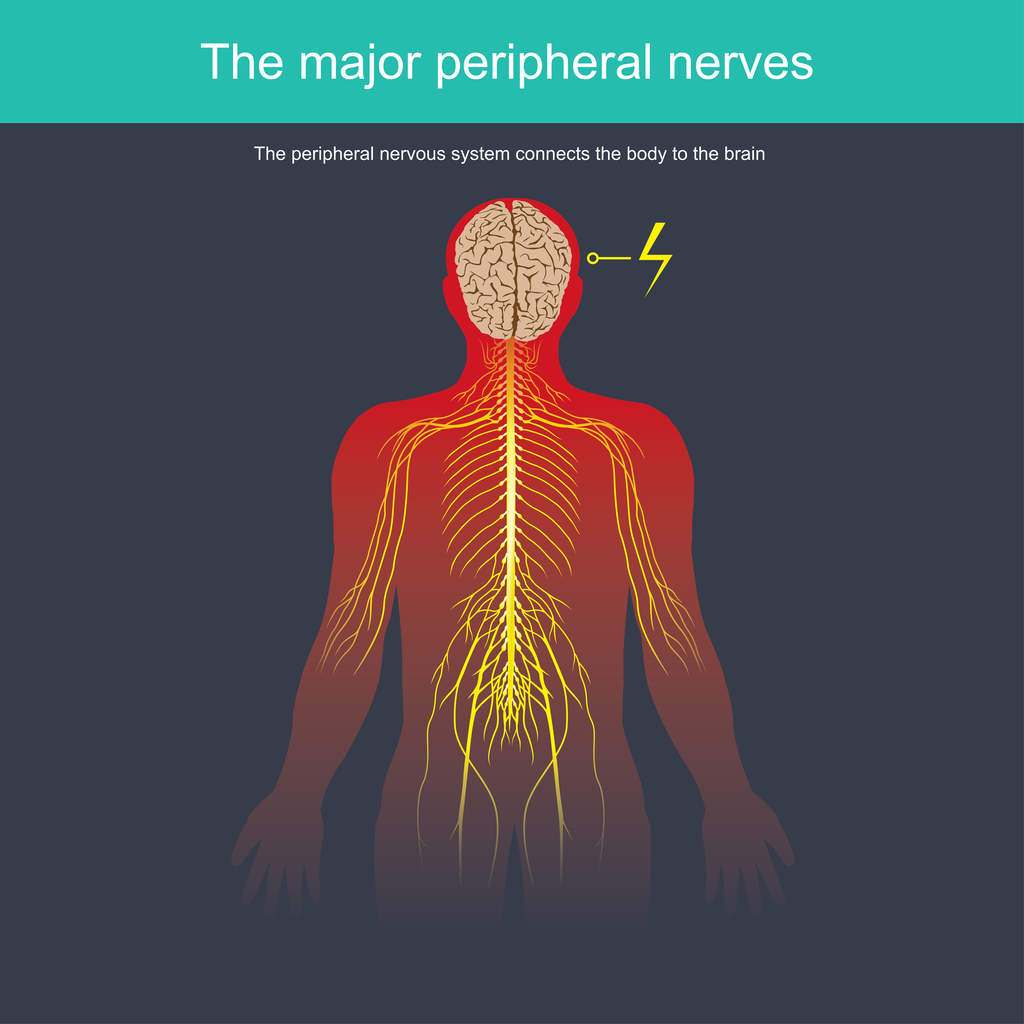
Neuropathic pain, or nerve pain, is caused when the nervous system is not working properly or becomes damaged. When GABA neurons are damaged, the body’s pain system does not function as it should, which contributes to neuropathic pain. Therefore, transplantation of GABA neurons may reduce neuropathic pain.
Transplanting
During GABAergic transplantation, embryonic cells from the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) of the brain are transplanted into the spinal cord. The nervous system then integrates these cells, creating non-damaged GABA nerve cells. This is thought to help restore functioning of the body’s pain system.
Outcomes
Studies involving GABAergic transplantation in mice have had promising results in reduction of neuropathic pain. However, the transplantation is still in the preclinical phase for humans. Additional research and studies are needed to conclude the effectiveness of GABAergic transplants as a treatment for neuropathic pain.
Additional source: Science Daily