Pain
HCN2 Channel Blockers as an Emerging Treatment for Neuropathic Pain
What is neuropathic pain?
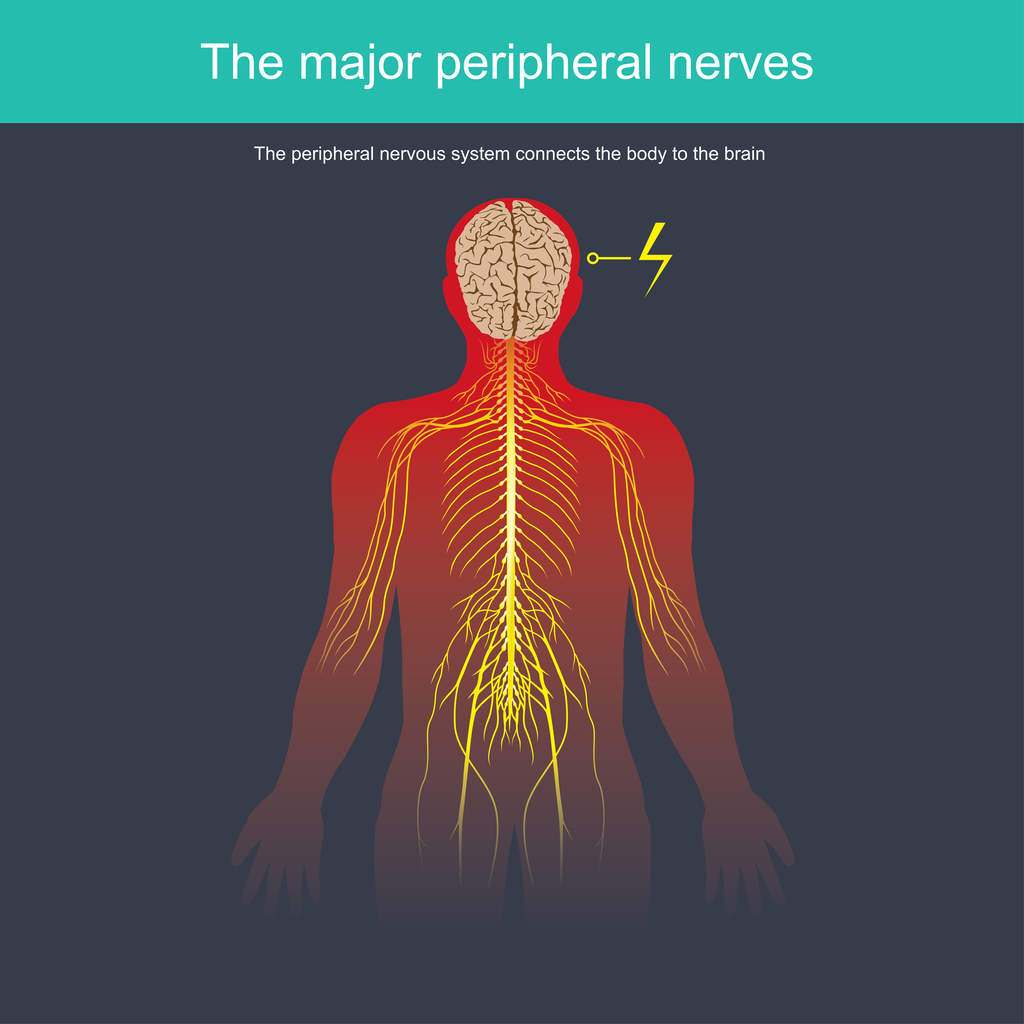
Neuropathic pain is a chronic pain condition that occurs due to nerve damage or a malfunctioning nervous system. The nervous system includes peripheral nerves, the brain, and the spinal cord. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nerves spread throughout the body and transfer information between the brain and spinal cord from other parts of the body. Nerve damage can change the nerve function at an injury site or the area surrounding an injury, causing them to send wrong signals to pain centers.
HCN2 Channel Blockers
Hyperpolarization-activated nucleotide (HCN) gated ion channels are found primarily in the brain, central nervous system, and heart. They play a part in regulating the electrical activities of neurons in the body. HCN ion channels have four isoforms, known as HCN1, HCN2, HCN3 and HCN4. HCN2 channels are expressed in the central nervous system and the heart. Research has shown that HCN2 channels may be related to pain receptors, as well as inflammatory and cellular factors, involved in neuropathic pain. Therefore, blocking HCN2 channels may reduce neuropathic pain.
Studies
Studies involving mice found that increased expression of HCN2 channels contributed to neuropathic pain and increased inflammatory factors. When HCN2 channels were blocked, those inflammatory factors significantly decreased, which reduced pain.
HCN2 channel blockers were also tested in mice with conditions similar to type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The blockers eliminated hypersensitivity to touch in the mice, suggesting that HCN2 may be an effective treatment for diabetic neuropathy in humans.
Conclusion
The current study involving HCN ion channel blockers in humans did not specifically focus on the HCN2 isoform. Additional research specifically involving HCN2 blockers are needed to determine if HCN2 channel blockers may be a viable treatment option for neuropathic pain.
Additional source: Pain Research Forum