Pain
Non-Medication Therapies for Back Pain

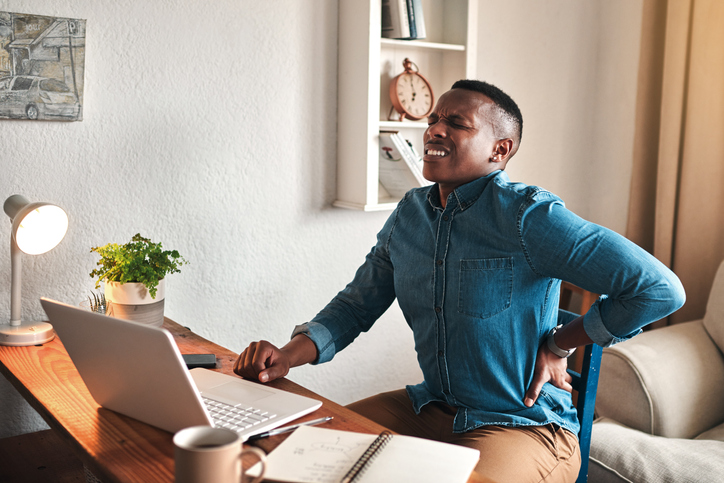
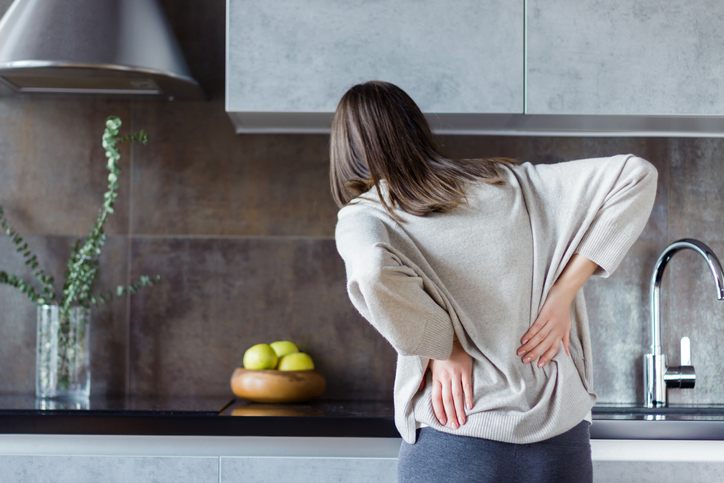
Back pain is a common health concern. Several non-medication therapies are available that can be used in conjunction with medication or, depending on the severity of pain, even instead of medication. These therapies are generally safe for most individuals and can significantly reduce or eliminate back pain.
Cold therapy
Cold therapy, such as applying ice packs or cold compresses to the back, can be used within the first 24 to 48 hours after pain begins to help reduce pain and swelling. Cold therapy should only be used for 15 to 20 minutes at a time. A thin layer, such as a towel, should always be placed between the skin and an ice pack to avoid causing skin damage.

Heat therapy
Using heat therapy, such as heating pads, a warm bath, or disposable heat packs, can reduce back pain in several ways. Heat improves circulation, increasing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, which can promote healing. It can decrease pain signals sent to the brain, decrease tension, and relax the muscles. Some individuals may find the most relief when alternating cold and heat therapy.

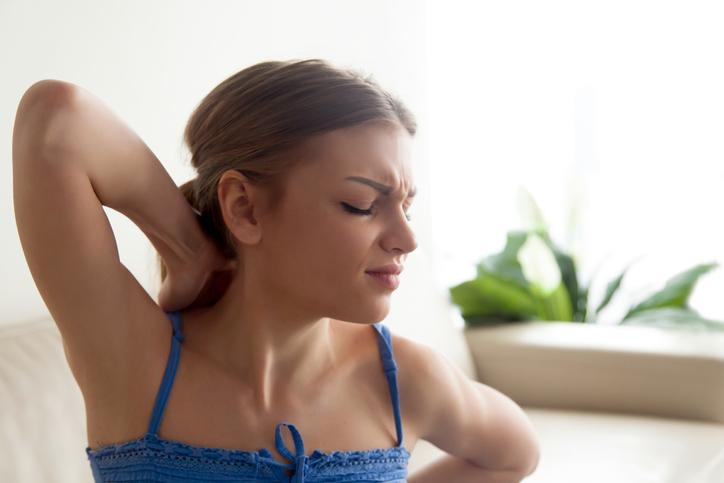
Massage therapy
Therapeutic massage can improve circulation and relieve painful muscle stiffness. It often improves flexibility and also causes the brain to release feel-good chemicals called endorphins. It can reduce overall stress and help promote better sleep, which is essential for pain relief.

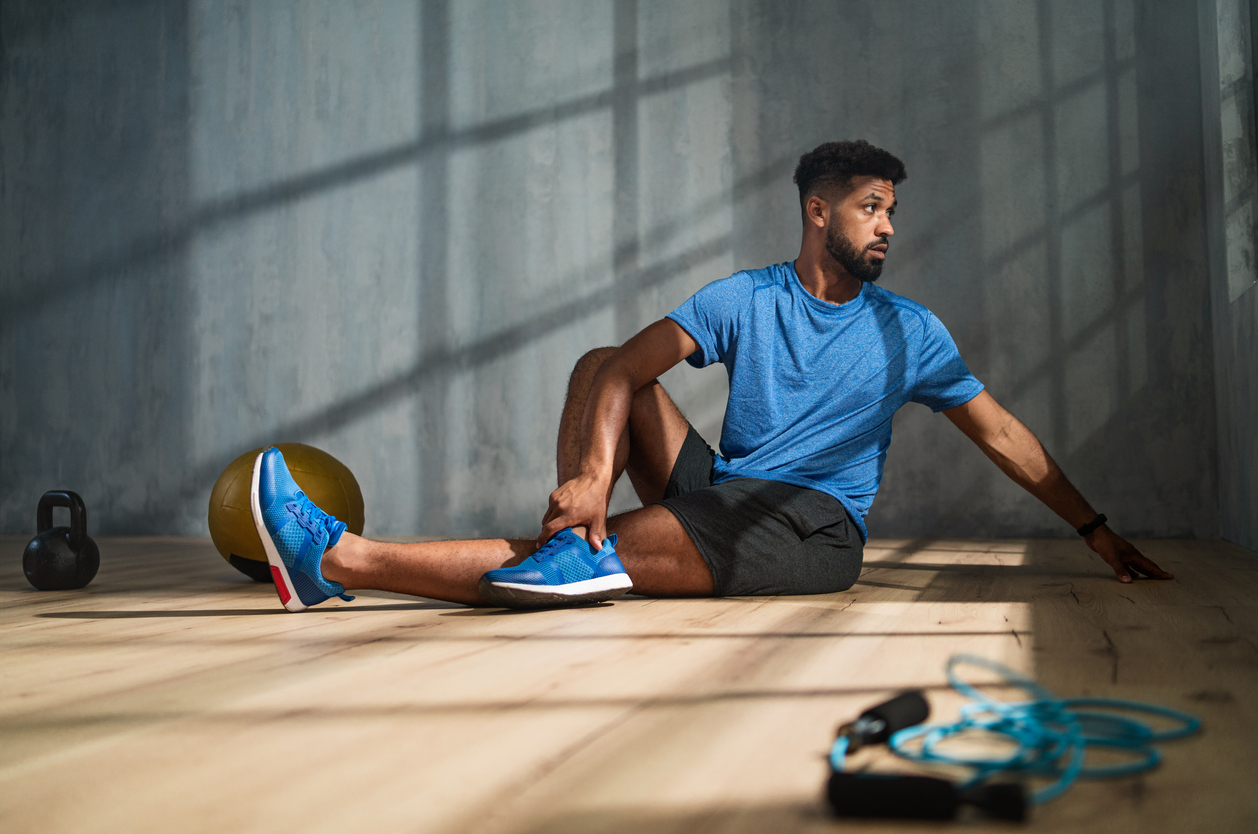
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can be extremely beneficial, especially for chronic back pain. A physical therapist can prescribe exercises that strengthen the core, including the muscles that support the spine. Physical therapy can also help improve posture and flexibility.

Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy
A TENS device contains electrodes that are placed on the back, which send low voltage electrical impulses along nerve fibers. The tingling sensation it provides can decrease pain. It may also stimulate the brain to release endorphins.