Pain
The Truth About Lower Back Pain
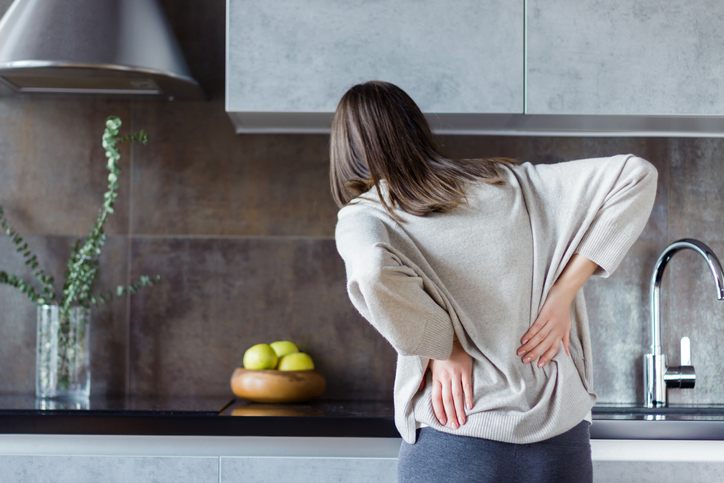
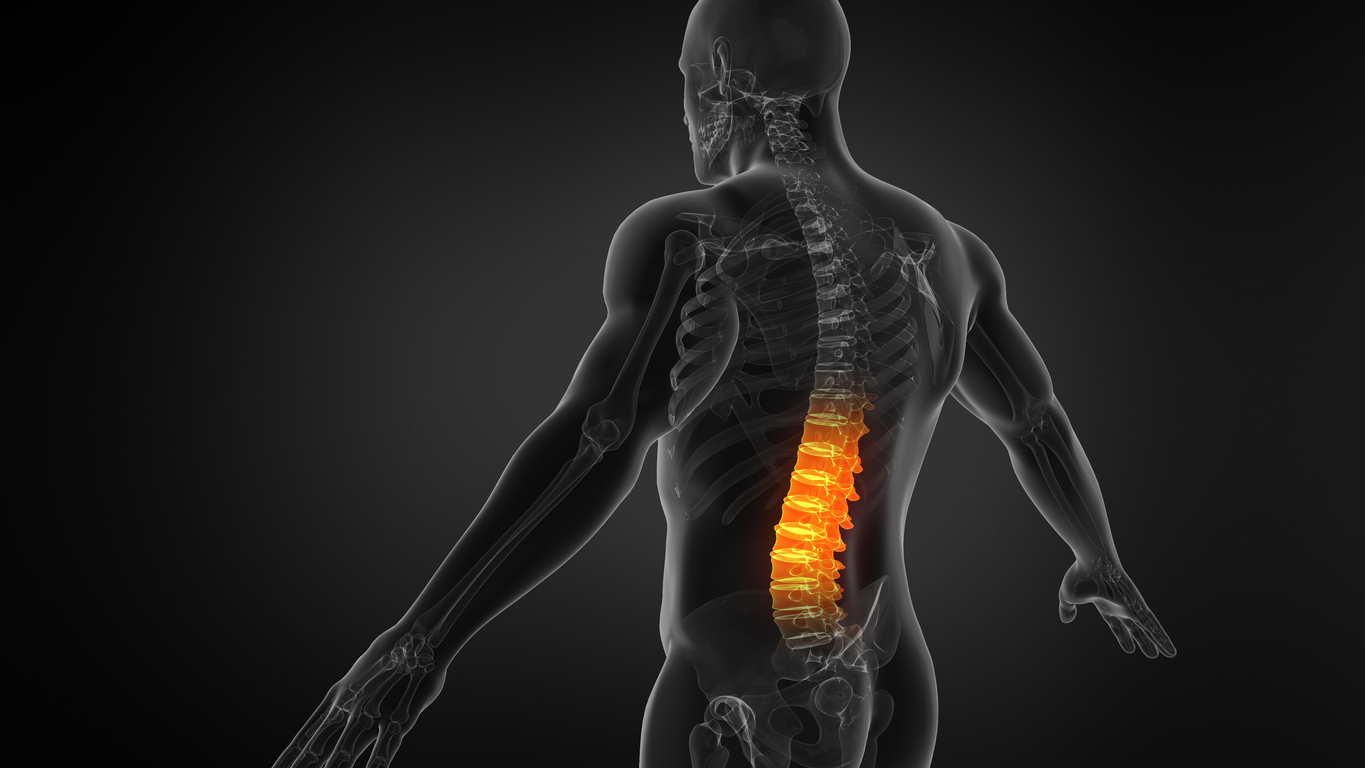
Almost everyone has low back pain at some point in their lives. Pain in the lower back, otherwise known as the lumbar region, is one of the top causes of being absent from work. Acute back pain typically occurs suddenly and often follows an injury, such as sports or heavy lifting. Pain which lasts longer than three months is considered chronic.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the underlying cause of lower back pain. The pain can be dull and achy, stinging and burning, or stabbing and shooting. It can also move from the lower back, to the thighs, and sometimes into the lower legs or feet. It can increase gradually or may occur suddenly.
Muscle spasms and tightness in the lower back may also transpire. Pain may worsen following prolonged sitting or standing. Difficulty can occur when standing, walking, or rising from a seated position. Symptoms that require urgent care include loss of bowel or bladder control, numbness in the groin area, leg weakness, fever, or pain when coughing or urinating.
Causes
Back pain following heavy lifting is usually caused by muscle strain. Excessive activities at the gym or while playing golf may also lead to low back pain.
A herniated disc is often to blame for low back pain. The vertebrae are padded by gel-like discs that are worn down by injuries and the passage of time. A weak disc may rupture or bulge, causing pressure on the spinal nerve roots. This can cause immense pain. If a bulging or ruptured disc puts pressure on the sciatic nerve, pain may run down one leg. This is known as sciatica.
Other causes of back pain may include lifting, pulling, or doing anything that contorts the spine. Carrying a heavy bag may cause a strain on the lower back.
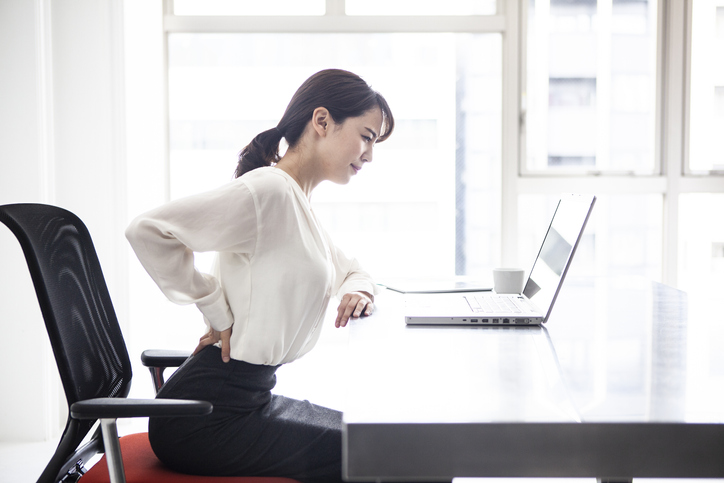
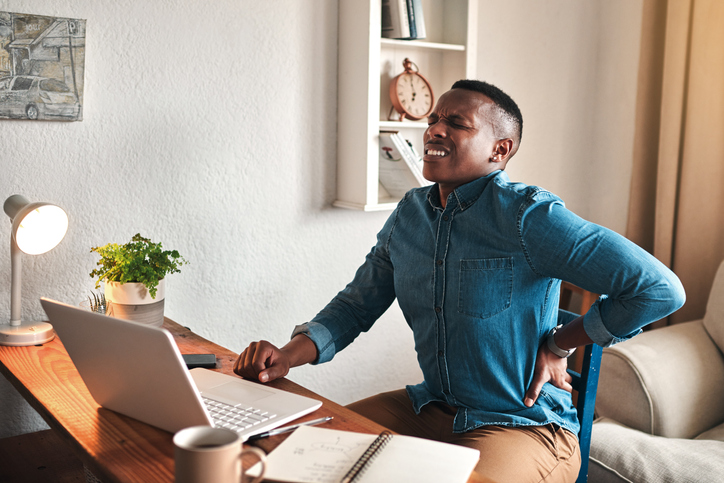
Sitting at a desk all day may also result in lower back pain, particularly if the chair is uncomfortable or slouching occurs. Good posture prevents strains on the lower back. It is important to have good lumbar support and other ergonomics when sitting, as well as evenly balancing your weight on your feet when standing.
There are also a number of chronic conditions that may lead to low back pain. Spinal stenosis may decrease the amount of space surrounding the spinal cord, which can put pressure on the spinal nerves. Spondylitis causes chronic back pain and stiffness because of severe inflammation of the spinal joints. Fibromyalgia also causes muscle aches and back pain.
Risks
The chance to experience low back pain increases with age. Many people begin to experience back pain in their 30s. Other reasons for low back pain include being overweight, being sedentary, or lifting heavy items while at work.
Treating back pain
Back pain caused by muscle strain often resolves itself, but measures can be taken to increase comfort, such as a heating pad or warm baths. Though bed rest may be beneficial at first, most physicians recommend returning to normal activities as quickly as possible. Research indicates that more than a day or two of rest may actually worsen the pain and reduce muscle tone and flexibility. Including Yoga as part of a treatment regimen may decrease the amount of low back pain.
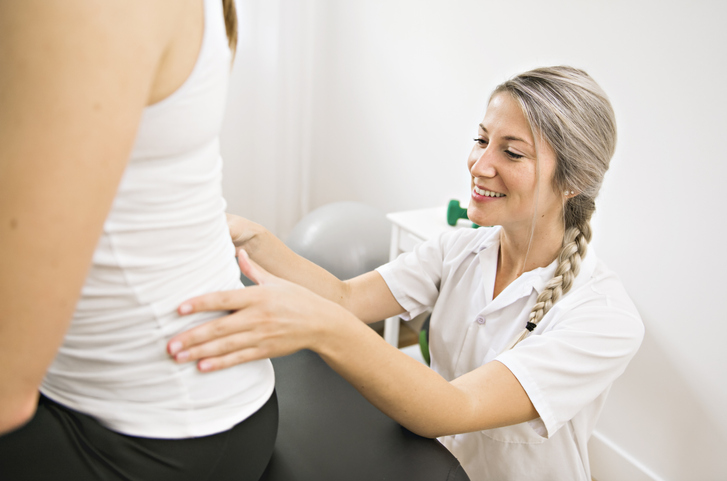
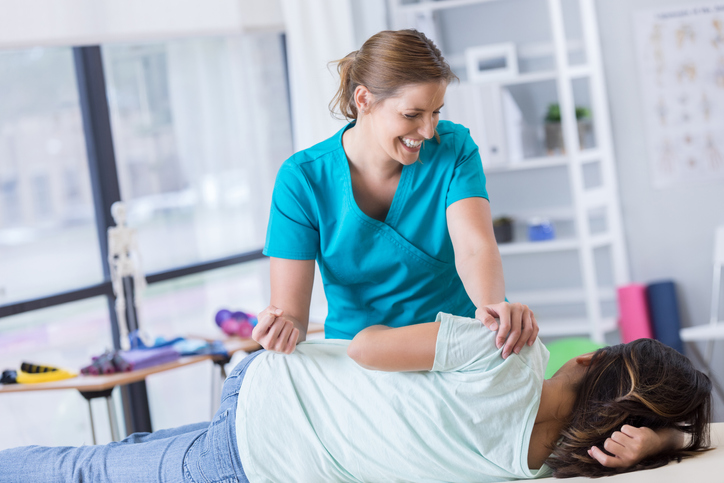
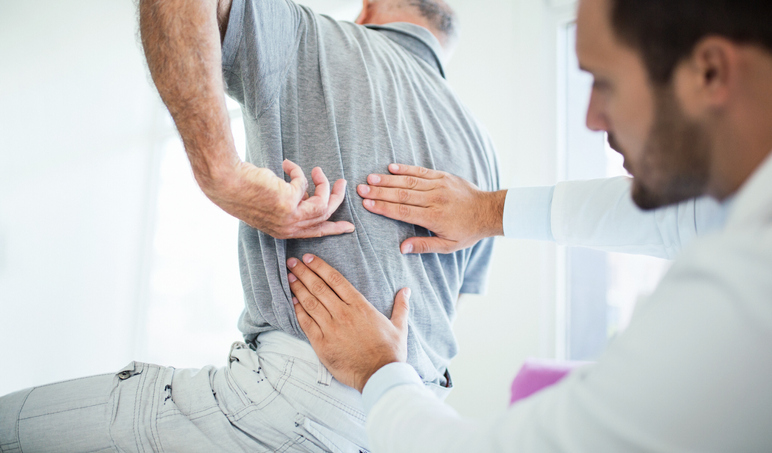
Spinal manipulation conducted by chiropractors and osteopathic doctors may treat low back pain by applying pressure to bones and surrounding tissues. Massage therapy may also be helpful when combined with physical activity and stretching.
Medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen, as well as pain-relieving creams, may be suggested for muscle aches. For more severe pain, a health care professional may recommend prescription medication.
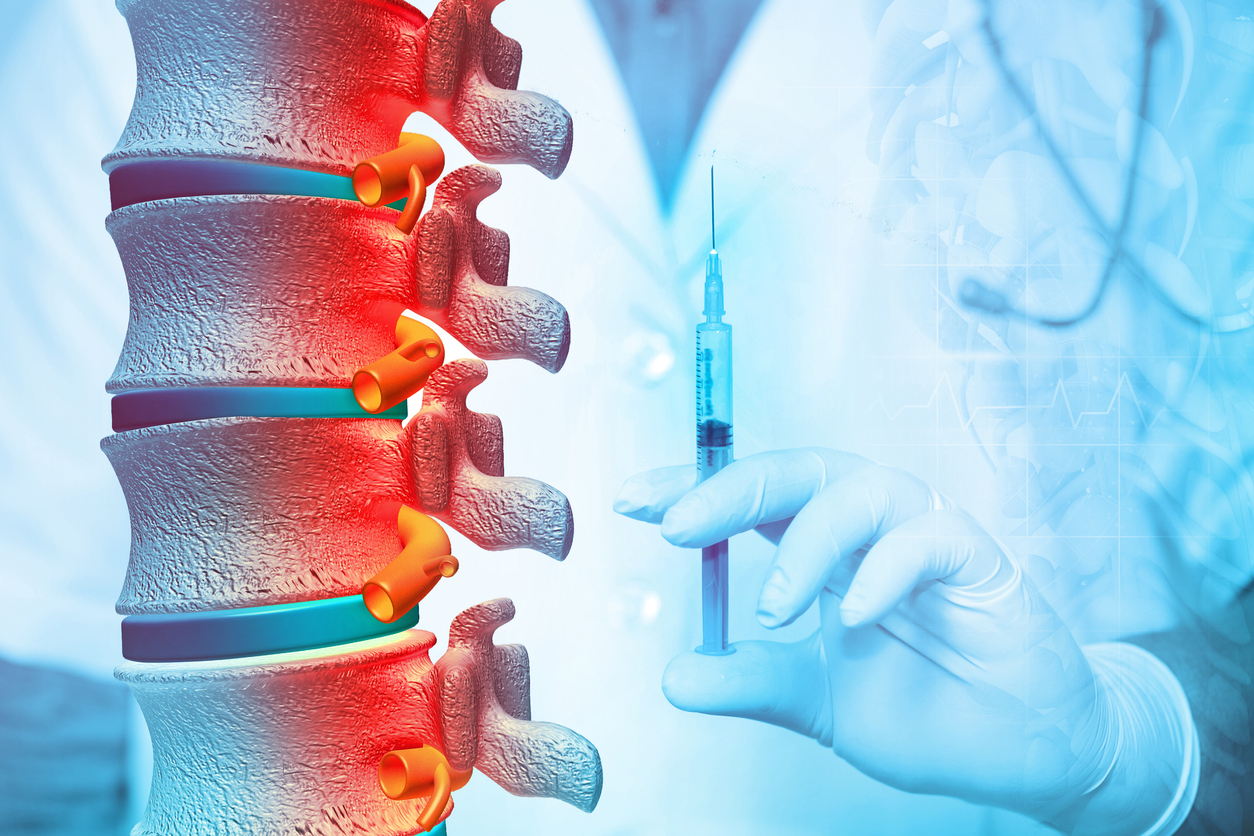
If other therapies and medications are ineffective, a physician may recommend injections, such as a nerve root block, which targets irritated nerves. Injections usually contain steroid medication, which reduces inflammation.
Surgery may be recommended if other treatments have not been successful in treating lower back pain. Depending on the cause of pain, a surgeon may remove a herniated disc, increase the space around the spinal cord, or fuse two spinal vertebrae together.
Inactivity for an extended period of time can be treated by a rehabilitation program that will strengthen the muscles and help individuals return to their daily routine. A couple of strength-training motions that may help the lower back are flexion and extension exercises. It is beneficial to do physical activities that are safe.
Prevention
To prevent low back pain, it is recommended to maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, lift with the legs and not the back, and make sure posture is optimal while at work.