Pain
The Stages of Lyme Disease

What is Lyme Disease?
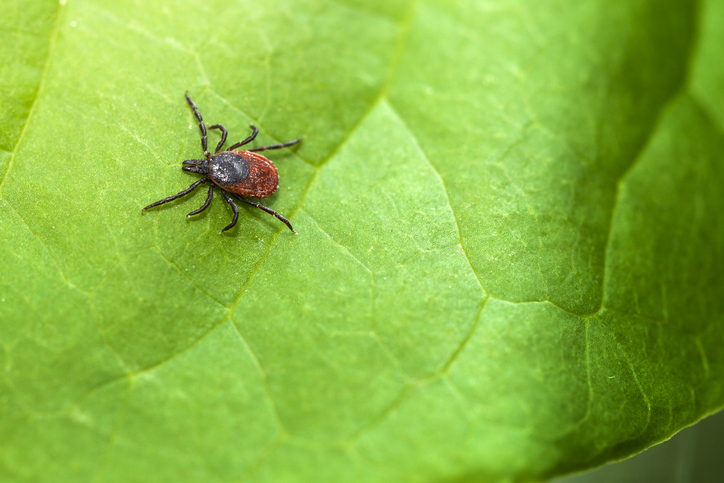
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Borrelia. The bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia mayonii are responsible for Lyme disease in North America. In Europe and Asia, Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii are responsible for Lyme disease. The bacteria is spread to humans via the bite of an infected tick, usually a black-legged tick (commonly known as a deer tick).
Stages of Lyme disease
Lyme disease is categorized into three stages: early localized Lyme disease, early disseminated Lyme disease, and late disseminated Lyme disease. Symptoms depend on the stage of the disease.
Stage 1: Early localized Lyme disease
Early localized Lyme disease can occur anywhere from 3 to 30 days after the tick bite. Symptoms include, but are not limited to, the following:
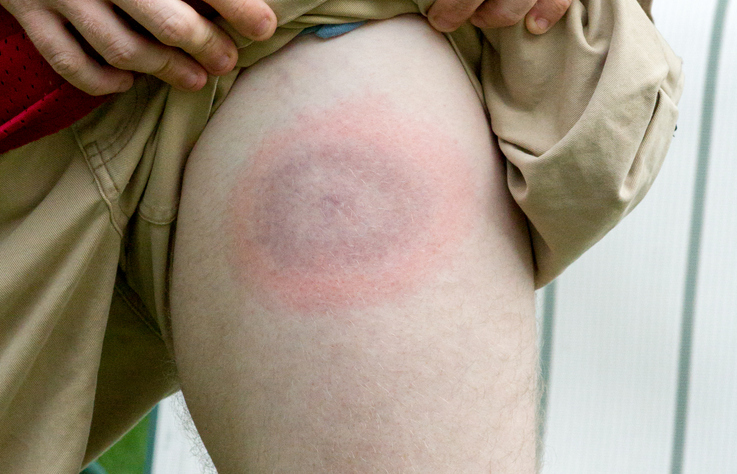
- Red, “bulls-eye” type rash, otherwise known as erythema migrans, appears at the site of the tick bite.
- The rash is warm to the touch but is typically not itchy or painful.
- The rash can reach up to 12 inches in diameter.
- The rash disappears after 4 weeks.
Stage 2: Early disseminated Lyme disease
Early disseminated Lyme disease can develop days to weeks after a tick bite. Symptoms of stage 1 and stage 2 can overlap. Stage 2 is characterized by flu-like symptoms, including the following:
- Chills
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Headaches
- Vision changes
- Rash, which may appear in other areas
- Neurological symptoms, such as numbness and tingling
- Bell’s palsy
- Heart palpitations or chest pain
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
Stage 3: Late disseminated Lyme disease
Late disseminated Lyme disease can develop if the infection was not treated in stage 1 or stage 2. It can occur months or even years after the initial tick bite. Symptoms include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Severe headaches
- Arthritis in one or more joints
- Disturbances in heart rhythm
- Brain disorders, such as encephalopathy
- Short-term memory loss
- Sleep difficulties
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mental fogginess
- Numbness in the arms, legs, hands or feet
- Speech problems
- Abnormal muscle movements
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness and tingling