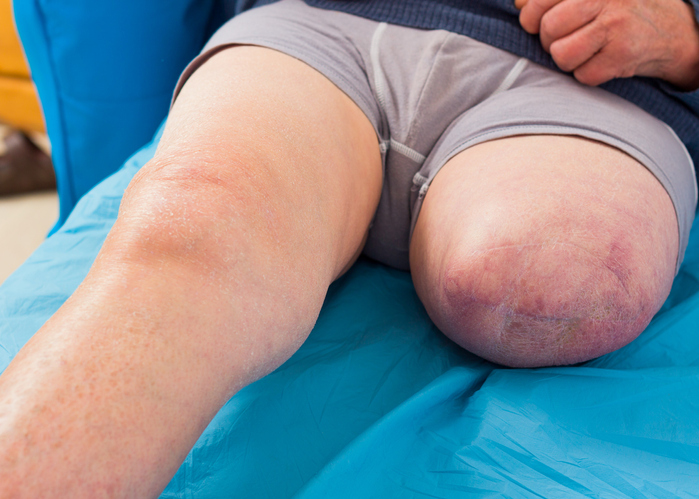
Pain
Inflammation and Chronic Pain
What is inflammation?
Inflammation occurs when the immune system sends out inflammatory cells as a response to an irritant. These cells trap the irritant to help the body heal. Inflammation can repair injuries and protect against germs, viruses, bacteria, foreign objects, etc., to keep the body safe; however, too much inflammation can result in chronic pain.
Types of inflammation
There are two types of inflammation. Acute is short-lived and chronic is long-lasting. Acute inflammation usually goes away within hours to days and is most commonly caused by sudden body damage. Chronic inflammation can last for months or years and results when the body continues to send inflammatory cells when there are no irritants involved.
Inflammation and pain
Inflammation is a symptom of many chronic pain conditions. With an autoimmune disease (also called a chronic inflammatory disease), the immune system triggers inflammation when there are no outside invaders to ward off. The body cannot differentiate between foreign cells and its own cells; therefore, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body.
When this occurs for long periods, healthy tissue, cells and organs can become damaged. This can result in internal scarring and tissue death. It can also cause joint irritation, swelling, and loss of cartilage.
Additionally, inflammation can lead to diseases or pain. Prolonged inflammation can also increase the risk of developing the following:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune disease)
- Obesity
- Cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Asthma
- Cognitive decline or dementia
- Heart Disease
Symptoms
Acute inflammation typically has obvious symptoms, including redness, warmth, pain and swelling. However, chronic inflammation has subtler symptoms that can be resilient, which may include the following:
- Persistent infections
- Changes in weight
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Anxiety or depression
- Body pain
Causes
Inflammation begins when the body starts to fight against harmful irritants. The most common causes of inflammation include the following:
- Germs, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi
- Untreated acute inflammation
- Injuries, such as scraping or damaging the body with foreign objects
- Autoimmune disorders
- Radiation effects
- Long-term exposure to polluted air or chemicals
Risk factors
There are certain factors that increase the risk of developing inflammation, which include the following:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Chronic stress
- Alcohol use