Pain
What Is Vertebrogenic Pain?

What is vertebrogenic pain?
Vertebrogenic pain occurs when vertebral endplates in the spine become worn or damaged. Vertebral endplates are located on the interface of both the top and bottom of each vertebra; they are the part of the vertebra that touch the intervertebral discs and serve as a protective layer to help disperse force on the spine. Until recently, most chronic lower back pain was attributed to arthritis or degenerative disc disease. However, new research finds that vertebral endplates have a considerable number of pain receptors that are connected to the basivertebral nerve, meaning low back pain can also be caused by damage to vertebral endplates.
Symptoms
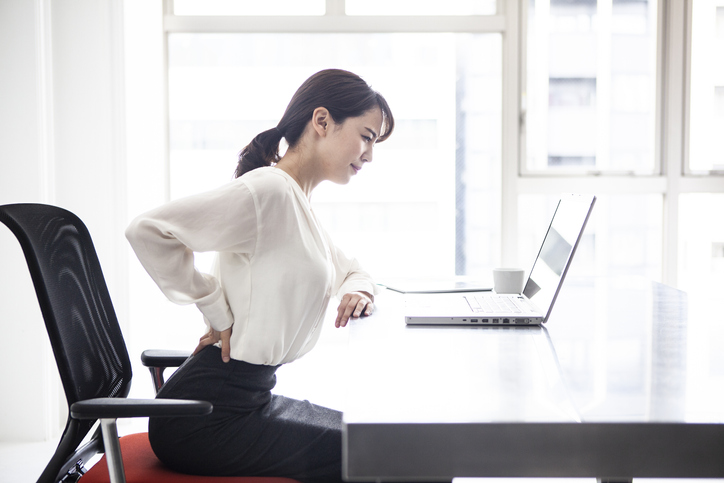
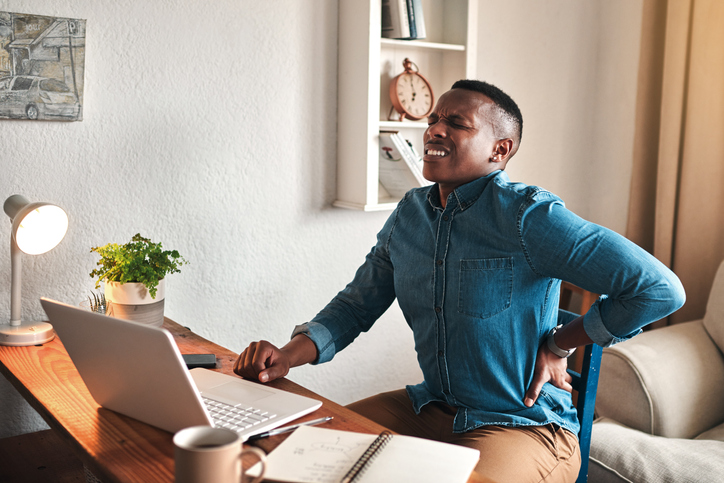
The primary symptom of vertebrogenic pain is low back pain. It is often described as deep, aching, or burning pain in the center of the low back. The pain may dissipate for several days and then flare again. It tends to be worse in the following situations:
- After sitting for extended periods
- During physical activity
- When bending forward
If an intervertebral disc is compressing the spinal cord, numbness, tingling, or weakness may also develop. Damage to vertebral endplates can also cause referred pain in other areas of the body, most likely in the gluteal region.
Causes
Vertebrogenic pain can be caused by trauma/injury or normal wear and tear.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of vertebrogenic pain include the following:
- Tall in stature
- Obesity
- Family history of chronic back pain
- Physically demanding jobs/careers
- Smoking
- Trauma/falls
- Over the age of 40