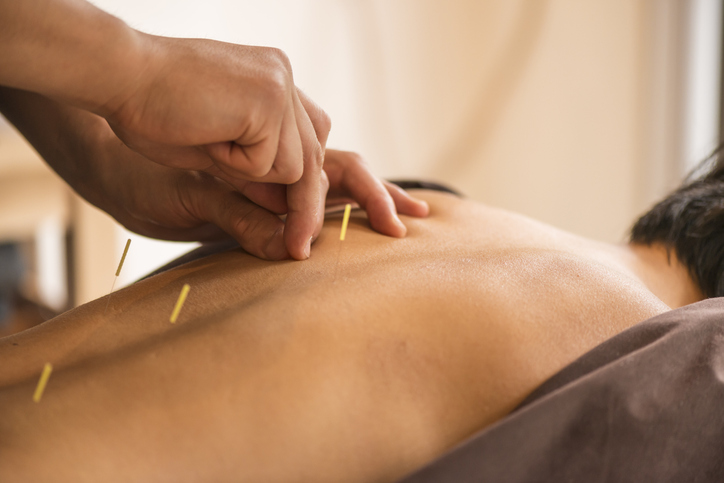
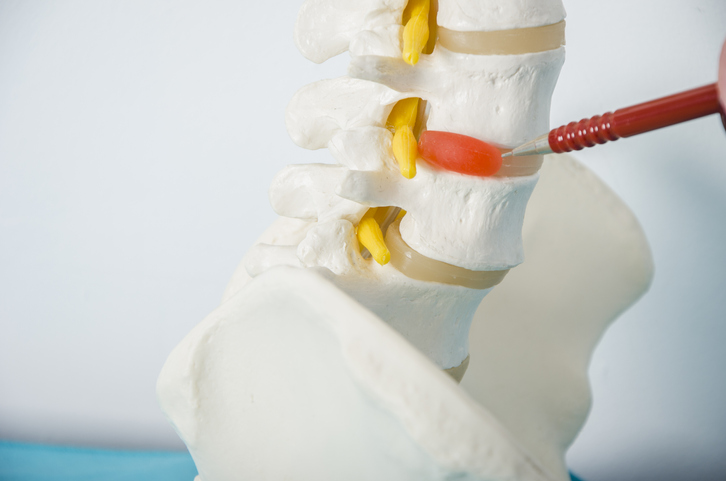
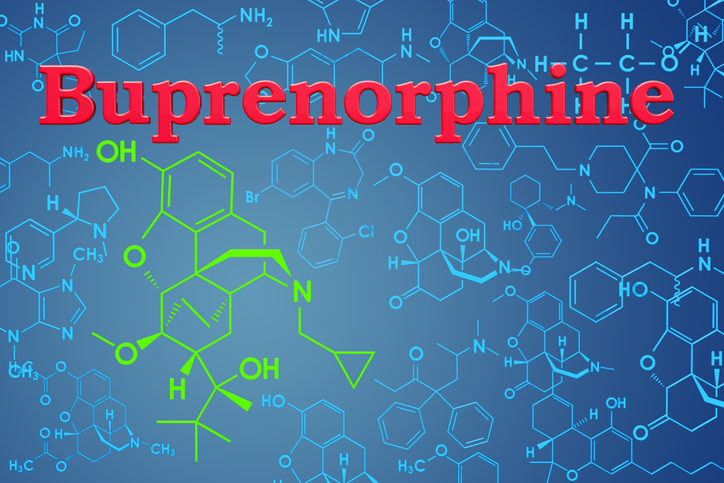
Treatments
Medications for Herniated Disc Pain

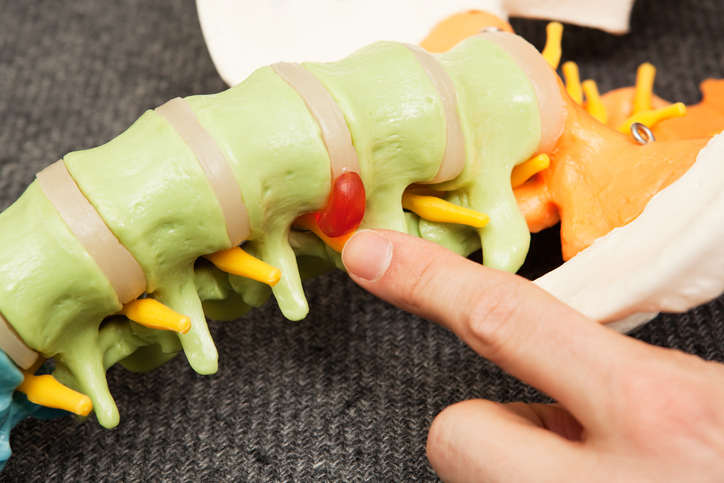
What is a herniated disc?
A herniated disc (or disk) is also referred to as a slipped or ruptured disc. Spinal discs are rubbery cushions that sit between individual vertebrae. As a disc naturally degenerates with age, the soft jelly-like center of the disc (nucleus) can herniate or tear through the tougher, rubbery exterior (annulus). This can occur at any point of the spine, but the most common location is between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae in the lower back.
Conventional medical treatment
The medical treatment of a herniated disc is highly individualized and depends on pain severity, specific symptoms, and the initial cause of the herniated disc. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain and other symptoms. A spine specialist can help determine the best treatment or combination of treatments.
Medications
Medication may be used to treat discomfort and pain of a herniated disc for up to six weeks. They include the following:
- Over-the-counter pain medications may be recommended for mild to moderate pain. This includes acetaminophen, ibuprofen or naproxen. These medicines can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation; however, they should not be used for more than 10 days unless directed by a health care professional. If pain persists or becomes severe, additional medication may be prescribed.
- Prescription non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, work the same way as those that can be purchased over-the-counter medicine. The difference is the strength of the tablet. If over-the-counter NSAIDs do not ease pain, a health care professional can prescribe a stronger dose.
- Oral steroids may be prescribed to decrease inflammation and relieve pain. This medication should be used short-term. Prolonged use has multiple adverse effects.
- Muscle relaxers can help if muscle spasms are present. Muscle spasms often accompany a herniated disc. This medication may cause dizziness.
- Nerve pain medications, such as amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, pregabalin and tramadol can help ease pain caused by nerve damage. These medications work by suppressing nerve activity.
- Antidepressants are sometimes prescribed to treat pain caused by a herniated disc. They work by blocking pain messages in the brain. They also increase endorphins, which are “feel-good” hormones.
- Opioid medication may be prescribed for short-term use if other medications fail to relieve pain. They can ease intense or severe pain. Examples include codeine or an oxycodone-acetaminophen combination. Opioids can be addictive; therefore, caution should be used. Potential side effects of opioids include confusion, constipation, nausea and sedation.