Treatments
Types of Biofeedback
4 people found this helpful
Print
Share
Save
What is biofeedback?
Biofeedback is a type of therapy that involves the use of technology to monitor involuntary body responses, such as heart rate and perspiration, with the goal of learning to control these responses in order to improve a mental or physical health condition.
Types of biofeedback
There are several types of biofeedback. Each type measures different involuntary body functions/responses.
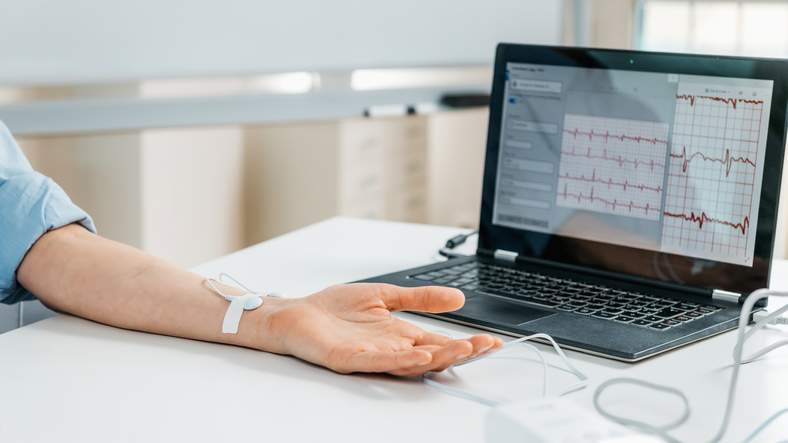
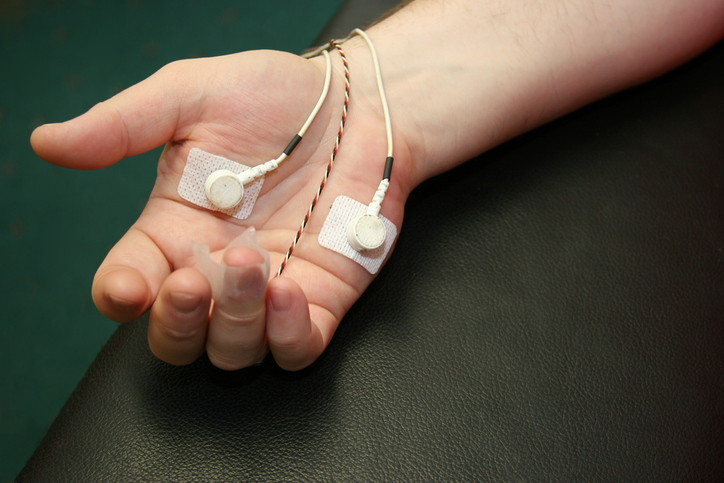
- Heart rate variability biofeedback measures the pulse and how the heart rate varies. Sensors are placed on the fingers or earlobes to measure blood volume changes. Learning to control heart rate can help treat symptoms of anxiety, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Electromyogram (EMG) biofeedback measures muscle tension. Sensors are typically placed on skeletal muscles to measure electrical activity that causes muscles to contract. It can be used for the treatment of headaches, back pain, or anxiety disorders.
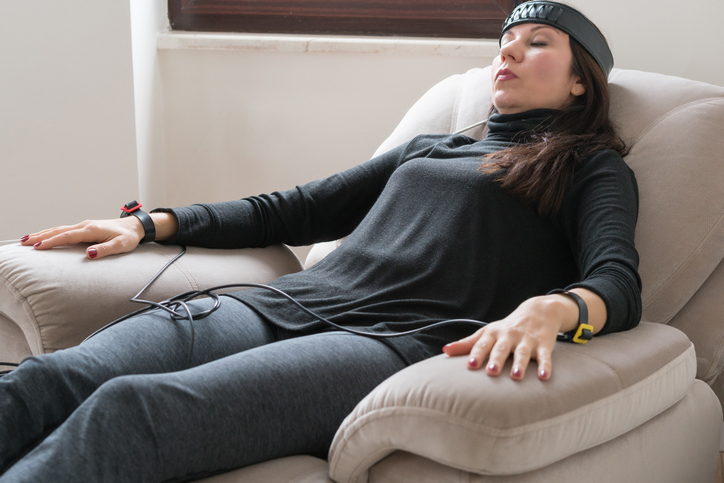
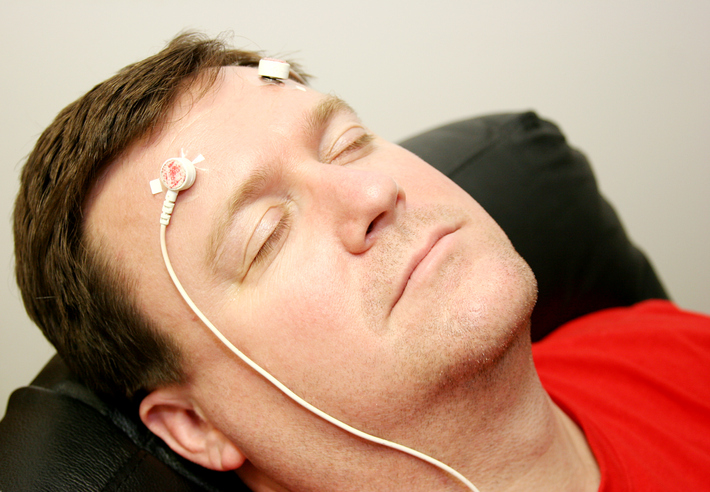
- Electroencephalography (EEG) biofeedback involves placing sensors on the scalp in order to measure brain wave activity during a set period. It is most commonly used as a treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and seizure disorders.
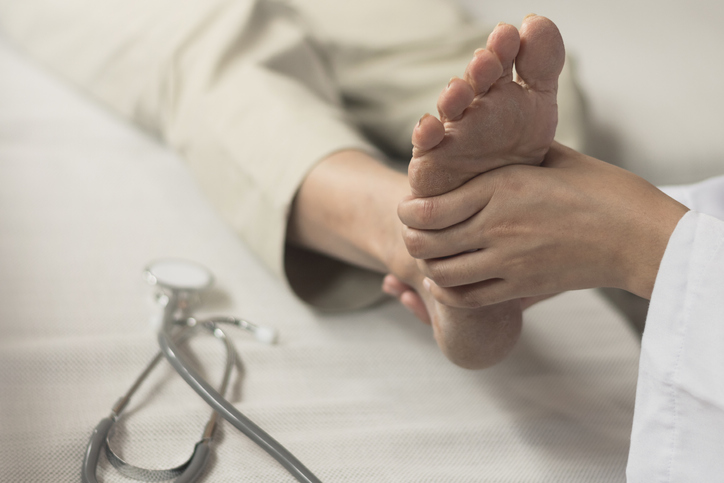
- Thermal biofeedback involves placing sensors on the fingers or feet to monitor temperature based on blood flow to the skin. It can help treat symptoms of anxiety disorders, headaches, or Raynaud’s disease.
- Electrodermal activity (EDA) biofeedback measures sweat gland activity and the amount of perspiration on the skin. Sensors are typically placed around the fingers or on the palms or wrists. Feedback based on sweat gland activity can be beneficial in the treatment of anxiety disorders or chronic pain.
The long-term goal of biofeedback therapy is to better manage involuntary physical responses associated with various mental and physical health conditions.