Treatments
Coping with Chronic Pain Using Cognitive Behavior Therapy
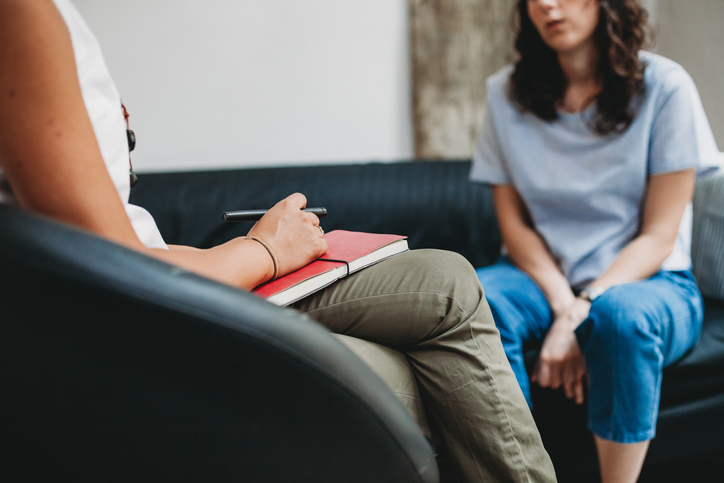

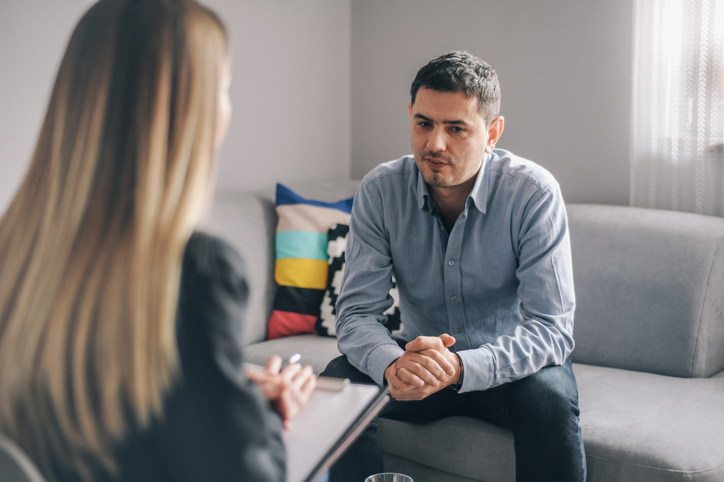
What is cognitive behavioral therapy?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT, is a common type of psychotherapy; it is a combination of cognitive therapy, which focuses on moods and thoughts, and behavioral therapy, which focuses on actions and behaviors. It involves learning how to identify and change inaccurate or negative thoughts and behavioral patterns in order to respond to stressful situations in a more effective way.
CBT is an effective treatment for various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder. It is beneficial for anyone learning to better manage stressful situations. CBT has also been linked to reduced pain perception.
The goal of cognitive behavioral therapy
CBT can address the destructive thought patterns that frequently accompany both chronic pain and depression. A therapist can help with identifying negative thoughts and replacing them with healthier thoughts. As negative thoughts and behaviors that are based on false perceptions are altered, the development of positive coping behaviors emerge.
By adopting calming thoughts, the mind and body can cope with chronic pain. Calming techniques include yoga, meditation, visualization, and progressive muscle relaxation. CBT helps change the way pain is viewed in order for the mind to better handle it.
Effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy
To better understand the practice of CBT, it's recommended to work with a counselor or therapist to reach certain goals. Once CBT is understood and practiced, therapy can be practiced alone. CBT influences thoughts by not thinking about the pain, but instead, focusing on the positive things in life.
Thoughts and depression
Chronic pain frequently causes feelings of sadness, anger and frustration. Due to the nature of chronic pain, social isolation, work issues, sleep disturbances, loss of independence, or financial problems can lead to low self-esteem, anxiety and depression. It is often a vicious cycle — pain causes heightened symptoms of depression, and depression causes increased pain sensitivity.
As depression worsens, the patterns influence the cognitive process, disrupting daily lifestyles. CBT helps change the inability to deal with negative cognitive patterns that lead to depression. It involves learning how to identify, understand and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that are linked to depression. It helps to recognize the problem and provides coping skills to reduce the symptoms of depression.