Pain
Treatment for Age-Related Back Pain

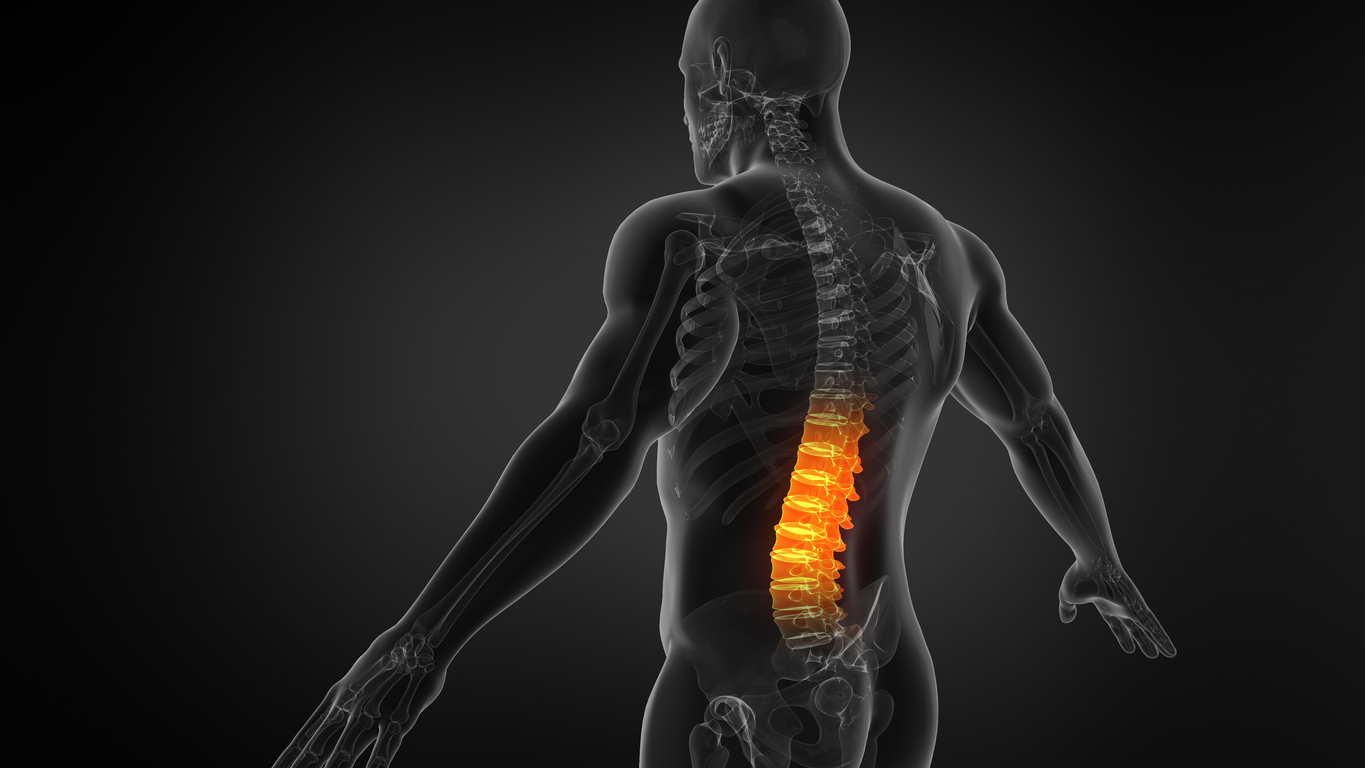
The spine of an average adult consists of 24 vertebrae (bones) that connect with facet joints. Discs are jelly-like cushions separating the bones of the spine (vertebrae). Ligaments stabilize the spine. During the aging process, discs lose fluid and become thinner. The vertebrae lose mineral content, resulting in thinner bones. The spinal column becomes compressed, resulting in curvature. Bone spurs may also develop on the vertebrae.
Aging and the spine
The spine begins to age in the 20s and 30s and continues to age throughout life. The natural process of aging causes the loss of bone mass or density. The bones lose calcium and other important minerals.
Three common reasons for age-related back pain
Spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and osteoarthritis are the three most common reasons for back pain after the age of 50. Osteoarthritis involves the gradual breakdown of cartilage in one or more joints. When the protective cushioning of cartilage deteriorates, the bones in the joint eventually rub together, causing inflammation and pain. Spinal stenosis occurs when the canal that encases the spinal cord becomes narrow due to thickened ligaments, arthritic facet joints, or disc degeneration. Spondylolisthesis occurs when one vertebra slips forward onto the vertebrae located below it.
Treatment options for age-related back pain
Oftentimes, chronic back pain is age related. However, there are ways to treat this pain. Treatment options for age-related back pain include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Physical activity
Physical activity plays an essential role in the treatment and prevention of back pain. Being physically active positively impacts the back and body in several ways. This could include low-impact aerobics, pool activities, yoga, and core-strengthening activities. - Pain relieving medications
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen, can reduce inflammation and pain. A health care professional can prescribe a stronger dosage if over-the-counter medications are ineffective. Analgesics and muscle relaxers can also relieve pain. - Physical therapy
Physical therapy can be extremely beneficial, especially for chronic back pain. A physical therapist can prescribe exercises that strengthen the core, including the muscles that support the spine. Physical therapy can also help improve posture and flexibility. - Temperature therapy
Heat therapy relaxes stiff joints and muscles; whereas, cold therapy numbs acute pain and reduces inflammation. Heat therapy increases the temperature of the targeted area, improving circulation and blood flow. Cold therapy is used to decrease blood flow to a targeted area, which can reduce inflammation and swelling. They should be no more than 20 minutes each hour. Switching between heat and cold therapy can help reduce certain types of pain; however, cold therapy should be used the first few days following an injury. . - Rest
When recovering from an injury, rest is needed to reduce inflammation. Incorporating gentle stretching into restful periods can speed up the recovery process. Orders from a health care professional should be followed concerning bed rest. Extended bed rest can be ineffective and may even worsen back pain or cause other health issues. - Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Traditional Chinese Medicine describes acupuncture as a way to balance the life force, or chi, by inserting needles into specific points (meridians) to correct any unbalance in the flow. Western medicine views acupuncture as a way to stimulate muscle, tissues and nerves in order to release the body's natural painkillers. - Mindfulness
Mindfulness is a type of meditation that involves using certain skills (e.g., guided imagery, meditation, journaling, breathing exercises, etc.) to focus on the present and observe inner thoughts and feelings without judgment. Depression, anxiety and stress are increased when too much time is spent thinking negatively, problem-solving, or planning. The goal of mindfulness is to promote relaxation, improve mental clarity, and manage stress. - Chiropractic
Chiropractic is a health profession that focuses on controlled force to a spinal joint. A trained specialist (chiropractor) aligns the musculoskeletal structure (especially the spine) through hands-on manipulation. Chiropractic care can improve range of motion, reduce nerve irritability, help physical function, and decrease lower back pain.