Treatments
What to Expect With Whole Body Cryotherapy

What is cryotherapy?
Cryotherapy, also known as cryosurgery, is a treatment that involves the use of extreme cold to freeze and remove abnormal cells. Liquid nitrogen, liquid nitrous oxide, or argon gas is typically utilized to produce subzero temperatures. Normal cryotherapy is an in-office procedure that is minimally invasive.
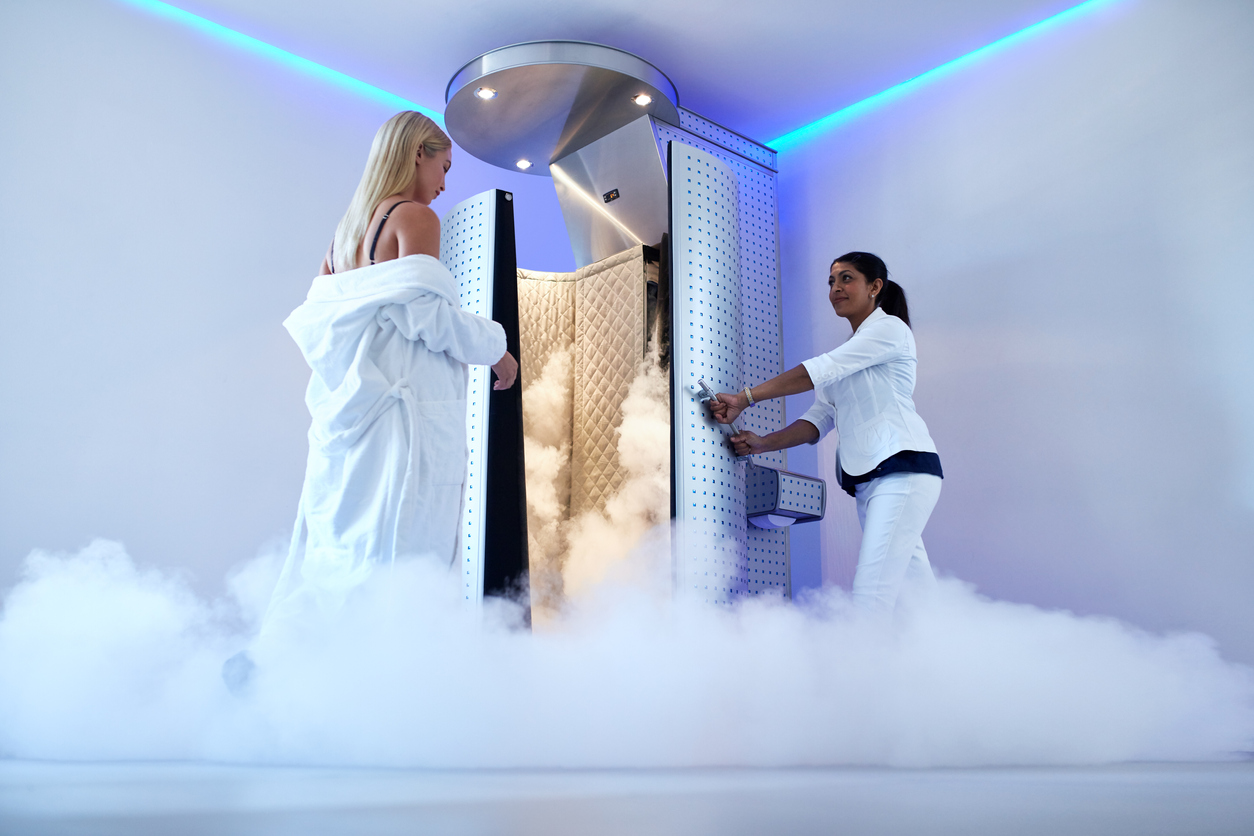
What is whole body cryotherapy?
Whole body cryotherapy (WBC) involves exposing the entire body to temperatures ranging from negative 200 to negative 300 degrees Fahrenheit (negative 129 to negative 184 degrees Celsius). This treatment typically lasts between two and four minutes. Whole body cryotherapy consists of standing in an enclosure that has an open top. The torso and legs stay inside the device and are exposed to extreme cold temperatures. Another method involves several people that sit or stand in a totally enclosed chamber. This includes the head and entire body being exposed for two to four minutes. Whole body cryotherapy should never be done alone and never exceed four minutes.
Benefits of whole body cryotherapy
Although The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved whole body cryotherapy or the devices used, many people claim it to be an effective treatment for various conditions. WBC advertises to be beneficial in helping with the following:
- Asthma
- Alzheimer's disease
- Anxiety
- Arthritis
- Chronic pain
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Migraines
- Multiple sclerosis
The process of whole body cryotherapy
Whole body cryotherapy can typically be done at gyms, spas, and wellness centers. The cryochamber, or tank, for WBC is cooled to extremely frigid temperatures with the use of liquid nitrogen. Most are shoulder height, so the head stays above the cryochamber. However, other devices involve the entire body being enclosed. Protective coverings for the ears (if completely enclosed), feet and hands should be worn. The exposure time is very limited, two to four minutes, due to the freezing temperature.
Risks of whole body cryotherapy
WBC has the potential to cause various risks. They include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Asphyxiation, especially when liquid nitrogen is used for cooling
- Hypoxia, or oxygen deficiency, when nitrogen vapors are added to a closed room
- Loss of consciousness
- Cold-induced rashes
- Frostbite
- Burns
- Eye injury from the extreme temperatures
As with any new therapy, consult a health care professional before attempting whole body cryotherapy. WBC may worsen certain conditions.